
Surface ectoderm
Подписчиков: 0, рейтинг: 0
| Surface ectoderm | |
|---|---|
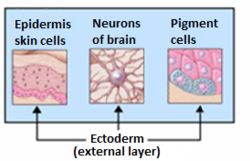 Organs derived from ectoderm.
| |
| Details | |
| Precursor | ectoderm |
| Identifiers | |
| FMA | 87656 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The surface ectoderm (or external ectoderm) forms the following structures:
- Skin (only epidermis; dermis is derived from mesoderm) (along with glands, hair, and nails)
- Epithelium of the mouth and nasal cavity and glands of the mouth and nasal cavity
- Tooth enamel (as a side note, dentin and dental pulp are formed from ectomesenchyme which is derived from ectoderm (specifically neural crest cells and travels with mesenchymal cells)
- Epithelium of anterior pituitary
- Lens, cornea, lacrimal gland, tarsal glands and the conjunctiva of the eye
- Apical ectodermal ridge inducing development of the limb buds of the embryo.
- Sensory receptors in epidermis
See also
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20071213145329/http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/martini10/chapter18/custom3/deluxe-content.html
- Coad, Jane; Dunstall, Melvyn (2001). Anatomy and physiology for midwives. Edinburgh; New York: Mosby. ISBN 0723429790.
|
Human embryonic development in the first three weeks
| |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Week 1 | |||||||||
| Week 2 (Bilaminar) |
|||||||||
| Week 3 (Trilaminar) |
|
||||||||