- Abrazo Scottsdale Campus
- Abrazo West Campus
- Advocate Christ Medical Center
- Advocate Good Samaritan Hospital
- Advocate Illinois Masonic Medical Center
- Advocate Sherman Hospital
- Alaska Native Medical Center
- Albany Medical Center
- Albert B. Chandler Hospital
- Allegheny General Hospital
- Allegheny Health Network
- Anderson Regional Medical Center
- Antelope Valley Hospital
- Arrowhead Regional Medical Center
- Ascension Providence Hospital, Novi Campus
- Ascension St. Mary's Hospital
- Ascension Via Christi Hospital in Pittsburg
- Ascension Via Christi St. Francis
- Atlanta Medical Center
- Atrium Health Wake Forest Baptist
- Augusta University Medical Center
- Aultman Hospital
- Ball Memorial Hospital
- Banner - University Medical Center Phoenix
- Banner Desert Medical Center
- Banner Lassen Medical Center
- Banner University Medical Center Tucson
- Baptist Memorial Hospital-Golden Triangle
- Barnes-Jewish Hospital
- Bayhealth Medical Center
- Baylor Scott & White Medical Center – Temple
- Baylor University Medical Center
- Baystate Health
- Beaumont Hospital, Royal Oak
- Bellevue Hospital
- Benefis Health System
- Ben Taub Hospital
- Berkshire Medical Center
- Bethesda North Hospital
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
- Billings Clinic
- Boston Medical Center
- Bridgeport Hospital
- Brigham and Women's Hospital
- Bronson Methodist Hospital
- Brookdale University Hospital and Medical Center
- Brooke Army Medical Center
- Butterworth Hospital
- Butterworth Hospital (Michigan)
- Cabell Huntington Hospital
- California Hospital Medical Center
- Capital Health Regional Medical Center
- Carilion Roanoke Memorial Hospital
- Carolinas Medical Center
- Catholic Medical Center
- Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
- Central Maine Medical Center
- Chandler Regional Medical Center
- Charleston Area Medical Center
- Cheyenne Regional Medical Center
- Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
- CHI St. Alexius Health Bismarck
- Christiana Hospital
- CHRISTUS Trinity Mother Frances Health System
- Cleveland Clinic
- Cleveland Clinic Akron General
- Community Regional Medical Center
- Concord Hospital
- Conemaugh Health System
- Cooper University Hospital
- Crozer Health
- Danbury Hospital
- Deaconess Hospital
- Del Sol Medical Center
- Denton Regional Medical Center
- Denver Health Medical Center
- Detroit Receiving Hospital
- Duke University Hospital
- Eastern Maine Medical Center
- ECU Health Medical Center
- Einstein Medical Center Philadelphia
- Elliot Hospital
- Ephraim McDowell Regional Medical Center
- Erie County Medical Center
- Fairview Hospital
- Firelands Regional Medical Center
- Flagstaff Medical Center
- Froedtert Hospital
- Geisinger Health System
- Geisinger Medical Center
- George Washington University Hospital
- Good Samaritan Hospital
- Grady Memorial Hospital
- Grand Strand Medical Center
- Grant Medical Center
- Greenville Memorial Hospital
- Guthrie Robert Packer Hospital
- Harborview Medical Center
- Harlem Hospital Center
- Hartford Hospital
- HCA Florida Kendall Hospital
- Hennepin County Medical Center
- Henry Ford Allegiance Health
- Henry Ford Hospital
- Henry Mayo Newhall Memorial Hospital
- Highland Hospital
- Hillcrest Hospital
- HonorHealth Scottsdale Osborn Medical Center
- Howard University Hospital
- Huntington Hospital
- Hurley Medical Center
- Indiana University Health Methodist Hospital
- Inova Fairfax Hospital
- Intermountain Medical Center
- J.W. Ruby Memorial Hospital
- Jackson Memorial Hospital
- Jacobi Medical Center
- Jamaica Hospital Medical Center
- Jefferson Abington Hospital
- Jefferson Torresdale Hospital
- Jersey City Medical Center
- Jersey Shore University Medical Center
- John Peter Smith Hospital
- Kaweah Delta Medical Center
- Kettering Health Dayton
- Kettering Health Main Campus
- Labette Health
- Lahey Hospital & Medical Center
- Lakeview Regional Medical Center
- Lancaster General Hospital
- Landstuhl Regional Medical Center
- Lawrence General Hospital
- Legacy Emanuel Medical Center
- Lehigh Valley Hospital–Cedar Crest
- Lima Memorial Health System
- List of trauma centers in the United States
- Logan Health
- Loma Linda University Medical Center
- Long Beach Memorial Medical Center
- Los Angeles General Medical Center
- Los Robles Hospital & Medical Center
- Lowell General Hospital
- Loyola University Medical Center
- Lutheran Hospital of Indiana
- Maine Medical Center
- Major trauma centre
- Massachusetts General Hospital
- McKay-Dee Hospital
- McLaren Flint
- Medical Center of the Rockies
- Medical City Dallas Hospital
- Medical City Plano
- MedStar Washington Hospital Center
- Memorial Hermann–Texas Medical Center
- Memorial Hospital of South Bend
- Memorial Medical Center
- Memorial Regional Hospital (Florida)
- Mercy Health - St. Vincent Medical Center
- Mercy Hospital
- Mercy San Juan Medical Center
- Methodist Dallas Medical Center
- Metro Health Hospital
- Miami Valley Hospital
- Morristown Medical Center
- Mount Carmel East
- Munson Medical Center
- MUSC Health University Medical Center
- MyMichigan Medical Center-Midland
- Nassau University Medical Center
- Natividad Hospital
- Naval Medical Center Camp Lejeune
- Northeast Georgia Medical Center Gainesville
- North Memorial Health Hospital
- North Shore University Hospital
- Norwalk Hospital
- NYU Langone Hospital – Brooklyn
- NYU Langone Hospital – Long Island
- Ogden Regional Medical Center
- Ohio State East Hospital
- Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center
- Oregon Health & Science University Hospital
- Orlando Regional Medical Center
- OSF Saint Anthony Medical Center
- Overland Park Regional Medical Center
- Pali Momi Medical Center
- Palomar Medical Center
- Parkland Memorial Hospital
- Parkview Medical Center
- Penn Presbyterian Medical Center
- Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center
- Penrose Hospital
- Pikeville Medical Center
- Poudre Valley Hospital
- ProMedica Defiance Regional Hospital
- ProMedica Toledo Hospital
- Providence Alaska Medical Center
- Providence Holy Cross Medical Center
- Queen of the Valley Medical Center
- Reading Hospital
- Regions Hospital
- Renown Regional Medical Center
- Rhode Island Hospital
- Richmond University Medical Center
- Riverside Methodist Hospital
- Riverside University Health System Medical Center
- Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital
- Ronald Reagan UCLA Medical Center
- Saint Elizabeth Community Hospital
- Saint Francis Hospital & Medical Center
- Saint Louis University Hospital
- Sanford USD Medical Center
- Santa Clara Valley Medical Center
- Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital
- San Joaquin General Hospital
- Scripps Mercy Hospital
- Self Regional Healthcare
- Sharp Memorial Hospital
- Sierra Vista Regional Medical Center
- Sinai-Grace Hospital
- Sky Ridge Medical Center
- Soin Medical Center
- Southwest General Health Center
- South Shore Hospital
- South Texas Health System Mcallen
- Sparrow Hospital
- St. Anthony Hospital
- St. Christopher's Hospital for Children
- St. Cloud Hospital
- St. Elizabeth Medical Center
- St. Francis Medical Center
- St. George Regional Hospital
- St. Joseph's Regional Medical Center
- St. Luke's University Health Network
- St. Mark's Hospital (Utah)
- St. Mary's Medical Center
- St. Mary Medical Center
- St. Rita's Medical Center
- St. Vincent Evansville
- St. Vincent Hospital
- St. Vincent Indianapolis Hospital
- Stamford Hospital
- Staten Island University Hospital
- Stony Brook University Hospital
- Stormont Vail Health
- Strong Memorial Hospital
- Summa Akron City Hospital
- Swedish Health Services
- Tampa General Hospital
- Temple University Hospital
- Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital Dallas
- ThedaCare Regional Medical Center–Neenah
- The Medical Center of Aurora
- The Queen's Medical Center
- Thomas Jefferson University Hospital
- Trident Medical Center
- Trinity Hospital
- Tripler Army Medical Center
- Tuba City Regional Health Care Corporation
- Tufts Medical Center
- UAMS Medical Center
- UC Davis Medical Center
- UF Health Jacksonville
- UF Health Shands Hospital
- Union Hospital
- University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center
- University Medical Center
- University Medical Center New Orleans
- University Medical Center of El Paso
- University Medical Center of Southern Nevada
- University of Colorado Hospital
- University of New Mexico Hospital
- University of Tennessee Medical Center
- University of Texas Medical Branch
- University of Utah Hospital
- UPMC Altoona
- UPMC Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh
- UPMC Mercy
- UPMC Presbyterian
- Upstate University Hospital
- UP Health System - Marquette
- UP Health System - Portage
- Utah Valley Hospital
- UW Health University Hospital
- Valleywise Health
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center
- Vassar Brothers Medical Center
- Ventura County Medical Center
- Walter Reed National Military Medical Center
- Weill Cornell Medical Center
- WellSpan Health
- Wellstar North Fulton Hospital
- Wentworth-Douglass Hospital
- Wesley Medical Center
- Westchester Medical Center
- Wheeling Hospital
- Womack Army Medical Center
Trauma center
A trauma center, or trauma centre, is a hospital equipped and staffed to provide care for patients suffering from major traumatic injuries such as falls, motor vehicle collisions, or gunshot wounds. A trauma center may also refer to an emergency department (also known as a "casualty department" or "accident and emergency") without the presence of specialized services to care for victims of major trauma.
In the United States, a hospital can receive trauma center status by meeting specific criteria established by the American College of Surgeons (ACS) and passing a site review by the Verification Review Committee. Official designation as a trauma center is determined by individual state law provisions. Trauma centers vary in their specific capabilities and are identified by "Level" designation: Level I (Level-1) being the highest and Level III (Level-3) being the lowest (some states have five designated levels, in which case Level V (Level-5) is the lowest).
The highest levels of trauma centers have access to specialist medical and nursing care, including emergency medicine, trauma surgery, critical care, neurosurgery, orthopedic surgery, anesthesiology, and radiology, as well as a wide variety of highly specialized and sophisticated surgical and diagnostic equipment. Lower levels of trauma centers may be able to provide only initial care and stabilization of a traumatic injury and arrange for transfer of the patient to a higher level of trauma care.
The operation of a trauma center is often expensive and some areas may be underserved by trauma centers because of that expense. As there is no way to schedule the need for emergency services, patient traffic at trauma centers can vary widely.
A trauma center may have a helipad for receiving patients that have been airlifted to the hospital. In some cases, persons injured in remote areas and transported to a distant trauma center by helicopter can receive faster and better medical care than if they had been transported by ground ambulance to a closer hospital that does not have a designated trauma center.
History
United Kingdom

Trauma centres grew into existence out of the realisation that traumatic injury is a disease process unto itself requiring specialised and experienced multidisciplinary treatment and specialised resources. The world's first trauma centre, the first hospital to be established specifically to treat injured rather than ill patients, was the Birmingham Accident Hospital, which opened in Birmingham, England in 1941 after a series of studies found that the treatment of injured persons within England was inadequate. By 1947, the hospital had three trauma teams, each including two surgeons and an anaesthetist, and a burns team with three surgeons. The hospital became part of the National Health Service in its formation in July 1948 and closed in 1993. The NHS now has 27 major trauma centres established across England, four in Scotland, and one planned in Wales.
United States
According to the CDC, injuries are the leading cause of death for American children and young adults ages 1–19. The leading causes of trauma are motor vehicle collisions, falls, and assaults with a deadly weapon.
In the United States, Robert J. Baker and Robert J. Freeark established the first civilian Shock Trauma Unit at Cook County Hospital in Chicago, Illinois on March 16, 1966. The concept of a shock trauma center was also developed at the University of Maryland, Baltimore, in the 1950s and 1960s by thoracic surgeon and shock researcher R Adams Cowley, who founded what became the Shock Trauma Center in Baltimore, Maryland, on July 1, 1966. The R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center is one of the first shock trauma centers in the world.Cook County Hospital in Chicago trauma center (opened in 1966). David R. Boyd interned at Cook County Hospital from 1963 to 1964 before being drafted into the Army of the United States of America. Upon his release from the Army, Boyd became the first shock-trauma fellow at the R Adams Cowley Shock Trauma Center, and then went on to develop the National System for Emergency Medical Services, under President Ford. In 1968 the American Trauma Society was created by various co-founders to include R Adams Cowley, Rene Joyeuse as they saw the importance of increased education and training of emergency providers and for nationwide quality trauma care.
Canada
According to the founder of the Trauma Unit at Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre in Toronto, Ontario, Marvin Tile, "the nature of injuries at Sunnybrook has changed over the years. When the trauma center first opened in 1976, about 98 percent of patients suffered from blunt-force trauma caused by accidents and falls. Now, as many as 20 percent of patients arrive with gunshot and knife wounds".
Fraser Health Authority in British Columbia, located at Royal Columbian Hospital and Abbotsford Regional Hospital, services the BC area, "Each year, Fraser Health treats almost 130,000 trauma patients as part of the integrated B.C. trauma system".
Definitions in United States
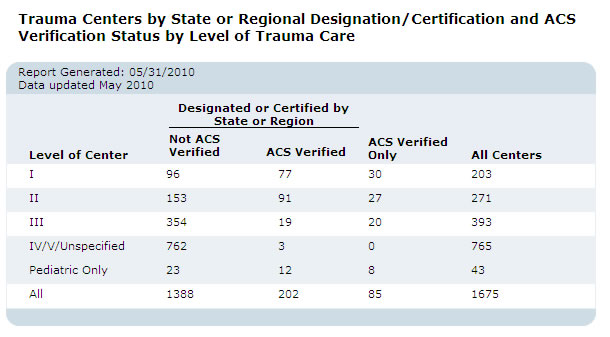
In the United States, trauma centers are ranked by the American College of Surgeons (ACS) or local state governments, from Level I (comprehensive service) to Level III (limited-care). The different levels refer to the types of resources available in a trauma center and the number of patients admitted yearly. These are categories that define national standards for trauma care in hospitals. Level I and Level II designations are also given adult or pediatric designations. Additionally, some states have their own trauma-center rankings separate from the ACS. These levels may range from Level I to Level IV. Some hospitals are less-formally designated Level V.
The ACS does not officially designate hospitals as trauma centers. Numerous U.S. hospitals that are not verified by ACS claim trauma center designation. Most states have legislation that determines the process for designation of trauma centers within that state. The ACS describes this responsibility as "a geopolitical process by which empowered entities, government or otherwise, are authorized to designate." The ACS's self-appointed mission is limited to confirming and reporting on any given hospital's ability to comply with the ACS standard of care known as Resources for Optimal Care of the Injured Patient.
The Trauma Information Exchange Program (TIEP) is a program of the American Trauma Society in collaboration with the Johns Hopkins Center for Injury Research and Policy and is funded by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. TIEP maintains an inventory of trauma centers in the US, collects data and develops information related to the causes, treatment and outcomes of injury, and facilitates the exchange of information among trauma care institutions, care providers, researchers, payers and policymakers.
Note that a trauma center is a hospital that is designated by a state or local authority or is verified by the American College of Surgeons.
Level I
A Level I trauma center provides the highest level of surgical care to trauma patients. Being treated at a Level I trauma center can reduce mortality by 25% compared to a non-trauma center. It has a full range of specialists and equipment available 24 hours a day and admits a minimum required annual volume of severely injured patients.
A Level I trauma center is required to have a certain number of the following people on duty 24 hours a day at the hospital:
- surgeons
- emergency physicians
- anesthesiologists
- nurses
- respiratory therapists
- an education program
- preventive and outreach programs.
Key elements include 24‑hour in‑house coverage by general surgeons and prompt availability of care in varying specialties—such as orthopedic surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, neurosurgery, plastic surgery, anesthesiology, emergency medicine, radiology, internal medicine, otolaryngology, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and critical care, which are needed to adequately respond and care for various forms of trauma that a patient may suffer, as well as provide rehabilitation services.
Most Level I trauma centers are teaching hospitals/campuses. Additionally, a Level I center has a program of research, is a leader in trauma education and injury prevention, and is a referral resource for communities in nearby regions.
Level II
A Level II trauma center works in collaboration with a Level I center. It provides comprehensive trauma care and supplements the clinical expertise of a Level I institution. It provides 24-hour availability of all essential specialties, personnel, and equipment. Oftentimes, level II centers possess critical care services capable of caring for almost all injury types indefinitely. Minimum volume requirements may depend on local conditions. Such institutions are not required to have an ongoing program of research or a surgical residency program.
Level III
A Level III trauma center does not have the full availability of specialists but has resources for emergency resuscitation, surgery, and intensive care of most trauma patients. A Level III center has transfer agreements with Level I or Level II trauma centers that provide back-up resources for the care of patients with exceptionally severe injuries (such as multiple trauma).
Level IV
A Level IV trauma center exists in some states in which the resources do not exist for a Level III trauma center. It provides initial evaluation, stabilization, diagnostic capabilities, and transfer to a higher level of care. It may also provide surgery and critical-care services, as defined in the scope of services for trauma care. A trauma-trained nurse is immediately available, and physicians are available upon the patient's arrival in the Emergency Department. Transfer agreements exist with other trauma centers of higher levels, for use when conditions warrant a transfer.
Level V
A Level V trauma center provides initial evaluation, stabilization, diagnostic capabilities, and transfer to a higher level of care. They may provide surgical and critical-care services, as defined in the service's scope of trauma care services. A trauma-trained nurse is immediately available, and physicians are available upon patient arrival in the emergency department. If not open 24 hours daily, the facility must have an after-hours trauma response protocol.
Pediatric trauma centers
A facility can be designated an adult trauma center, a pediatric trauma center, or an adult and pediatric trauma center. If a hospital provides trauma care to both adult and pediatric patients, the level designation may not be the same for each group. For example, a Level I adult trauma center may also be a Level II pediatric trauma center because pediatric trauma surgery is a specialty unto itself. Adult trauma surgeons are not generally specialized in providing surgical trauma care to children and vice versa, and the difference in practice is significant. In contrast to adult trauma centers, pediatric trauma centers only have two ratings, either level I or level II.
See also
- List of trauma centers in the United States
- Emergency medicine
- Trauma (medicine)
- Trauma surgery
- Trauma team
- Traumatology
External links
- Injury Prevention & Control: Trauma Care at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Trauma Centers Fact Sheet at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- Trauma Levels Explained, American Trauma Society
- FACS Verified Trauma Center Listing in the United States—American College of Surgeons
- Trauma Center Association of America, formerly known as the National Foundation for Trauma Care
- U.S. Trauma Center Crisis Report (2004)
- Report: U.S. Trauma Center Preparedness for a Terrorist Attack in the Community
- Report: Harris Poll: Trauma Care: Public's Knowledge and Perception of Importance 2004
- NHS England major trauma centres [1]
- NHS England 2012 major trauma centres map Urgent and emergency care services
- NHS England Ambulance trauma coding When to call 999
- NHS Wales trauma centres Accident and emergency departments
- NHS Scotland trauma centres list [2]
State trauma system regulation
- Bureau of Emergency Medical Services & Trauma System, Arizona Department of Health Services
- Arizona Trauma Center Designation
- Arizona Trauma System
- Georgia Trauma Commission
- PA Trauma Systems Foundation
- 25 Texas Administrative Code 157.125 (Texas Requirements for Trauma Facility Designation)
- Maryland Trauma System
| Principles | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment |
|
||||||||
| Management |
|
||||||||
| Pathophysiology |
|
||||||||
| Complications | |||||||||
|
Articles about hospitals
| |
|---|---|
| Common hospital components |
|
| Archaic forms |
|
| Geographic service area | |
| Complexity of services | |
| Unique physical traits | |
| Limited class of patients | |
| Funding | |
| Condition treated | |
| Century established | |