
Ulnar tunnel syndrome
| Ulnar tunnel syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Guyon's canal syndrome |
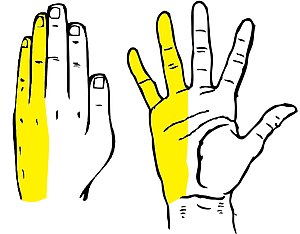 | |
| Cartoon depiction of classic ulnar sensory distribution, including mid-4th and 5th fingers. Note that this diagram does not portray hand muscles affected by ulnar neuropathy. | |
| Specialty |
Orthopedic surgery |
Ulnar tunnel syndrome, also known as Guyon's canal syndrome or Handlebar palsy, is caused by entrapment of the ulnar nerve in the Guyon canal as it passes through the wrist. Symptoms usually begin with a feeling of pins and needles in the ring and little fingers before progressing to a loss of sensation and/or impaired motor function of the intrinsic muscles of the hand which are innervated by the ulnar nerve. Ulnar tunnel syndrome is commonly seen in regular cyclists due to prolonged pressure of the Guyon's canal against bicycle handlebars. Another very common cause of sensory loss in the ring and pink finger is due to ulnar nerve entrapment at the cubital tunnel near the elbow, which is known as cubital tunnel syndrome.
Causes
While being idiopathic in some cases, causative factors of the ulnar tunnel syndrome include tumors, ganglion cysts, repetitive use, anatomical variations, and diseases of the neighboring blood vessels (thrombosis or aneurysm of the ulnar artery).
Diagnosis
Classification
Ulnar tunnel syndrome may be characterized by the location or zone within the Guyon's canal at which the ulnar nerve is compressed. The nerve divides into a superficial sensory branch and a deeper motor branch in this area. Thus, Guyon's canal can be separated into three zones based on which portion of the ulnar nerve are involved. The resulting syndrome results in either muscle weakness or impaired sensation in the ulnar distribution.
| Location | Symptoms | Associations | |
| Zone 1 | Proximal (prior to ulnar nerve bifurcation) | Mixed motor & sensory | Ganglia & hook of hammate fractures |
| Zone 2 | Surrounding deep motor branch ulnar nerve | Motor only | Ganglia & hook of hammate fractures |
| Zone 3 | Surrounding superficial sensory branch of ulnar nerve | Sensory only | Ulnar artery pathology |
Zone 2 type syndromes are most common, while Zone 3 are least common.
Treatment
Initial line of treatment is with anti-inflammatory drugs or cortisone injections. There have been trials with gloves which help protect the ulnar nerve from compression. The most radical treatment option is surgery to relieve tension in the volar carpal ligament which forms the roof of Guyon's canal, thereby reducing compression on the ulnar nerve.
See also
Further reading
- Slane, Josh; Timmerman, Mark; Ploeg, Heidi-Lynn; Thelen, Darryl G. (2011). "The influence of glove and hand position on pressure over the ulnar nerve during cycling". Clinical Biomechanics. 26 (6): 642–8. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2011.03.003. PMID 21458120.
- Maimaris, C; Zadeh, H G (1990). "Ulnar nerve compression in the cyclist's hand: Two case reports and review of the literature". British Journal of Sports Medicine. 24 (4): 245–6. doi:10.1136/bjsm.24.4.245. PMC 1478904. PMID 2097022.
- Rehak, David C. (Summer 2003). "Cyclist's Hands: Overcoming overuse injuries". Hughston Health Alert. Hughston Clinic.
- Bledsoe, Jim. "Cycling injuries - handlebar palsy". Sports Injury Bulletin.
- US patent 6845514, Yao, Joseph, "Protective device for the median and ulnar nerves", issued January 25, 2005
|
Diseases relating to the peripheral nervous system
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
