Welfare's effect on poverty
The effects of social welfare on poverty have been the subject of various studies.
Studies have shown that in welfare states, poverty decreases after countries adopt welfare programs. Empirical evidence suggests that taxes and transfers considerably reduce poverty in most countries whose welfare states commonly constitute at least a fifth of GDP. In 2013, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development asserted that welfare spending is vital in reducing the ever-expanding global wealth gap.
Table of effect

Timothy Smeeding used data from the Luxembourg Income Study to determine the effectiveness of anti-poverty and welfare programs on poverty reduction. The data for all the countries was from the year 2000 with the exception of the United Kingdom and the Netherlands for which the data was from 1999.
| Country | Social expenditures on non-elderly (as percentage of GDP) |
Total percent of poverty reduced |
|---|---|---|
|
|
2.3 | 26.4 |
|
|
9.6 | 65.2 |
|
|
11.6 | 77.4 |
|
|
7.3 | 70.5 |
|
|
5.8 | 46.0 |
|
|
10.9 | 69.7 |
|
|
7.1 | 60.1 |
|
|
9.3 | 76.9 |
|
|
7.4 | 75.8 |
|
|
4.3 | 57.7 |
|
|
5.5 | 44.1 |
| Average | 7.4 | 60.9 |
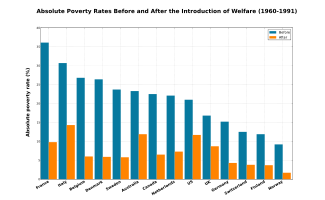
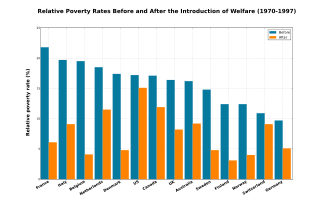
Table of poverty levels pre- and post-welfare
Two studies compare countries internationally before and after implementing social welfare programs. Using data from the Luxembourg Income Study, Bradley et al. and Lane Kenworthy measure the poverty rates both in relative terms (poverty defined by the respective governments) and absolute terms (poverty defined by 40% of United States median income), respectively. Kenworthy's study also adjusts for economic performance and shows that the economy made no significant difference in uplifting people out of poverty.
The studies look at the different countries from 1960 to 1991 (Kenworthy) and from 1970 to 1997 (Bradley et al.). Both these periods are roughly when major welfare programs were implemented such as the War on Poverty in the United States. The results of both studies show that poverty has been significantly reduced during the periods when major welfare programs were created.
| Country | Absolute poverty rate (1960–1991) (threshold set at 40% of United States median household income) |
Relative poverty rate
(1970–1997) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-welfare | Post-welfare | Pre-welfare | Post-welfare | |
|
|
23.7 | 5.8 | 14.8 | 4.8 |
|
|
9.2 | 1.7 | 12.4 | 4.0 |
|
|
22.1 | 7.3 | 18.5 | 11.5 |
|
|
11.9 | 3.7 | 12.4 | 3.1 |
|
|
26.4 | 5.9 | 17.4 | 4.8 |
|
|
15.2 | 4.3 | 9.7 | 5.1 |
|
|
12.5 | 3.8 | 10.9 | 9.1 |
|
|
22.5 | 6.5 | 17.1 | 11.9 |
|
|
36.1 | 9.8 | 21.8 | 6.1 |
|
|
26.8 | 6.0 | 19.5 | 4.1 |
|
|
23.3 | 11.9 | 16.2 | 9.2 |
|
|
16.8 | 8.7 | 16.4 | 8.2 |
|
|
21.0 | 11.7 | 17.2 | 15.1 |
|
|
30.7 | 14.3 | 19.7 | 9.1 |