- 23andMe
- 3did
- AAindex
- ABCdb
- ACLAME
- AgBase
- Allele Frequency Net Database
- Allen Brain Atlas
- All of Us (initiative)
- Alternative Splicing Annotation Project
- Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
- AnimalTFDB
- Antimicrobial Drug Database
- Aquatic Commons
- ArachnoServer
- ARDB
- AREsite
- Artade
- ASD (database)
- ASPicDB
- Atlas of UTR Regulatory Activity
- Autophagy database
- BacMap
- BacMet
- Bangladesh Fisheries Information Share Home
- Barcode of Life Data System
- BASys
- Beta-Lactamase Database (BLAD)
- Beta-Lactamase Database (BLDB)
- BGMUT
- BindingDB
- Bio2RDF
- BioCatalogue
- Biocuration
- BioGRID
- Biological database
- Biological Magnetic Resonance Data Bank
- Biometrics use by the South African government
- BioModels
- Biomolecular Object Network Databank
- Biomolecule Stretching Database
- BioNumbers
- BioPlex
- BitterDB
- Bovine Metabolome Database
- BrainMaps
- Brain atlas
- BRENDA tissue ontology
- Brix (database)
- BYKdb
- CADgene
- Calypso Ichthyological Database
- Cambridge Structural Database
- CancerResource
- Carbohydrate Structure Database
- Caribherp
- CATH database
- CBMAR
- Cellosaurus
- Cervical Cancer Gene Database
- CGView
- CharProtDB
- ChEBI
- ChEMBL
- ChemSpider
- ChimerDB
- China Kadoorie Biobank
- Ciliate MDS/IES database
- Ciona intestinalis protein database
- Circular RNA databases and resources
- Clinical Genome Resource
- ClinVar
- CLIPZ
- Co-occurrence network
- CollecTF
- Colocalization Benchmark Source
- COMBINE
- Combined DNA Index System
- Combrex
- Community Cyberinfrastructure for Advanced Microbial Ecology Research and Analysis
- Compendium of protein lysine acetylation
- Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database
- CompTox Chemicals Dashboard
- Conformational dynamics data bank
- ConoServer
- ConsensusPathDB
- Consensus CDS Project
- Conserved Domain Database
- COSMIC cancer database
- Crystallography Open Database
- Database for bacterial group II introns
- Database of Interacting Proteins
- Database of Molecular Motions
- Database of protein conformational diversity
- DataONE
- DB-ALM
- DBASS3/5
- DbCRID
- DbDNV
- DBTSS
- DcGO
- Death Domain database
- DECIPHER
- Department of Defense Serum Repository
- DIMA (database)
- DiProDB
- Disease Ontology
- DisProt
- DNA database
- DNA Data Bank of Japan
- Domine Database
- DPVweb
- DrugBank
- Dryad (repository)
- Early Detection Research Network
- East London Genes & Health
- EcoCyc
- Effective (database)
- EggNOG (database)
- Elsevier Biobase
- EMBiology
- EM Data Bank
- ENCODE
- Entrez
- Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource
- Eukaryotic Promoter Database
- European Genome-phenome Archive
- European Pollen Database
- Europe PubMed Central
- Evolutionary Classification of Protein Domains
- ExoCarta
- Exon-intron database
- Experimental factor ontology
- EzTaxon Database
- Families of Structurally Similar Proteins database
- FANTOM
- FARME
- FinnGen
- FishBase
- FloraBase
- FloraNT
- Flora Europaea
- FNAEG
- FooDB
- Fossilworks
- FREP
- Full-parasites
- Functional element SNPs database
- Fusarium graminearum genome database
- GeneDB
- Generation Scotland
- Genetic codes (database)
- Gene Ontology
- GigaDB
- GISSD
- Global microbial identifier
- GlycomeDB
- Golm Metabolome Database
- GPnotebook
- GreeNC
- GRIN (database)
- Guide to Pharmacology
- Gypsy (database)
- G protein-coupled receptors database
- H-Invitational
- Hazardous Substances Data Bank
- HIstome
- Histone Database
- HitPredict
- Homology-derived Secondary Structure of Proteins
- Human-transcriptome DataBase for Alternative Splicing
- Human Biomolecular Atlas Program
- Human Cell Atlas
- Human Metabolome Database
- Human Olfactory Data Explorer
- Human Protein Atlas
- Human Protein Reference Database
- Human Proteome Project
- HumHot
- Hymenoptera Genome Database
- IGRhCellID
- Index to Organism Names
- Indian Genetic Disease Database
- INTEGRALL
- Integrated Microbial Genomes System
- Interferome
- International Aging Research Portfolio
- International HapMap Project
- International Knockout Mouse Consortium
- International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium
- International Protein Index
- InterPro
- Intronerator
- Invasive Species Compendium
- IRefIndex
- Islander (database)
- IsoBase
- IUCN Red List
- Japanese Red List
- KaPPA-View4
- KEGG
- Ki Database
- L1Base
- LacED
- Laminin database
- LarvalBase
- Legume Information System
- LIPID MAPS
- List of biodiversity databases
- List of biological databases
- List of databases for oncogenomic research
- List of neuroscience databases
- List of Red Lists
- Living DNA
- LncRNAdb
- LocDB
- MANET database
- MANTIS Database
- Mapper(2)
- MatrixDB
- Medical Subject Headings
- MEDLINE
- Membranome database
- Merck Index
- MEROPS
- MESAdb
- MetaboLights
- Metabolite Set Enrichment Analysis
- Metabolomic Pathway Analysis
- MetaboMiner
- METAGENassist
- MICdb
- MimoDB
- MINAS
- Minimotif Miner
- MIPModDB
- MiRBase
- MiRGator
- MirGeneDB
- MiRNEST
- MiRTarBase
- MobiDB
- ModBase
- Model organism database
- Molecular Modeling Database
- Mouse Genetics Project
- Mouse Genome Informatics
- Mouse Phenome Database
- MUBII-TB-DB
- Multi-Omics Profiling Expression Database
- Munich Information Center for Protein Sequences
- MvirDB
- MyExperiment
- National DNA database
- National DNA Data Bank of Canada
- National Institute of Genetics
- NCBI Epigenomics
- NCI-Nature Pathway Interaction Database
- Neotoma Paleoecology Database
- NetPath
- Network of Cancer Genes
- NeuroLex
- NeuroNames
- Neuroscience Information Framework
- New Zealand Nationally Significant Collections and Databases
- NeXtProt
- NIAID ChemDB
- Non-B database
- NONCODE
- NucleaRDB
- Nucleosome positioning region database
- OMPdb
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Animals
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man
- Open protein structure annotation network
- Open Regulatory Annotation Database
- Operon database
- OriDB
- Orientations of Proteins in Membranes database
- Orphanet
- OrthoDB
- Pan-European Species directories Infrastructure
- PANDIT (database)
- PANTHER
- ParameciumDB
- Pathema
- Pathway Commons
- Patome
- PATRIC
- PCRPi-DB
- PDBbind database
- PDBREPORT
- PDBsum
- PDBWiki
- PeptideAtlas
- PeroxiBase
- Peroxiredoxin classification index
- Pharmacogene Variation Consortium
- PharmGKB
- Phenol-Explorer
- Phenoscape
- PHOSIDA
- Phospho.ELM
- Phospho3D
- PhylomeDB
- PhytoPath
- PlantCollections
- Plant ontology
- Plant Proteome Database
- PlasMapper
- Plazi
- PmiRKB
- Polbase
- PolymiRTS
- Polymorphic simple sequence repeats database
- PolyQ (database)
- Popgenie
- PREDITOR
- PRINTS
- Probabilistic Approach for Protein NMR Assignment Validation
- ProGlycProt
- ProRepeat
- ProSAS
- PROSITE
- ProtCID
- Protected health information
- Protein-RNA interface database
- Protein Circular Dichroism Data Bank
- Protein Data Bank (file format)
- Protein Information Resource
- Protein Segment Finder
- Protein structure database
- Protein Structure Evaluation Suite & Server
- Proteome Analyst
- Proteomics Identifications Database
- Proteopedia
- Pseudogene (database)
- Pseudomonas Genome Database
- PSORTdb
- PubChem
- PubMed
- PubMed Central
- PubMed Central Canada
- RAC: Repository of Antibiotic resistance Cassettes
- Rat Genome Database
- Reactome
- Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Explorer and Tester
- Recode (database)
- RefDB (chemistry)
- RegTransBase
- RegulonDB
- REPAIRtoire
- RepTar (database)
- Reptile Database
- Resolution by Proxy
- RetrOryza
- Riken integrated database of mammals
- RNA-binding protein database
- RNA CoSSMos
- RNA helicase database
- SABIO-Reaction Kinetics Database
- ScerTF
- SCRIPDB
- SeaLifeBase
- Sequence Ontology
- Serum Metabolome Database
- SHIFTCOR
- ShiftX
- Signaling Gateway (website)
- SitEx
- Small Molecule Pathway Database
- SNPedia
- Snptstr (database)
- SoyBase Database
- SPIKE (database)
- Standards for Reporting Enzymology Data
- Stem cell lineage database
- Structural Classification of Proteins database
- Structure atlas of human genome
- SuperPose
- SuperSweet
- Systematic Protein Investigative Research Environment
- TargetScan
- TcoF-DB
- TDR Targets
- The Cancer Imaging Archive
- The Monarch Initiative
- TIGR plant repeat database
- TIGR plant transcript assembly database
- TMPad
- Toxin-antitoxin database
- Toxin and Toxin-Target Database
- TOXMAP
- Transient receptor potential channel-interacting protein database
- Transporter Classification Database
- TRNADB
- U-CARE
- U12 intron database
- Uberon
- UgMicroSatdb
- UniPROBE
- Univec
- UTRdb
- UTRome
- VectorBase
- VectorDB
- VetBact
- VFDB
- ViralZone
- VIRsiRNAdb
- Virus Pathogen Database and Analysis Resource
- Voltage-gated potassium channel database
- Volume Area Dihedral Angle Reporter
- WebGeSTer
- WikiPathways
- Worldwide Protein Data Bank
- Xenbase
- Yeastract
- Yeast Metabolome Database
- Yeast Promoter Atlas
- YersiniaBase
- YeTFaSCo
- Your Favorite Gene
- Zebrafish Information Network
- ZINC database
- ZOBODAT
- Biometric databases
- Ecological databases
- Fisheries databases
- Food databases
- Metabolomic databases
- Online taxonomy databases
- Sperm banks
Biological database
Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization (both cellular and chromosomal), clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures.
Biological databases can be classified by the kind of data they collect (see below). Broadly, there are molecular databases (for sequences, molecules, etc.), functional databases (for physiology, enzyme activities, phenotypes, ecology etc), taxonomic databases (for species and other taxonomic ranks), images and other media, or specimens (for museum collections etc.)
Databases are important tools in assisting scientists to analyze and explain a host of biological phenomena from the structure of biomolecules and their interaction, to the whole metabolism of organisms and to understanding the evolution of species. This knowledge helps facilitate the fight against diseases, assists in the development of medications, predicting certain genetic diseases and in discovering basic relationships among species in the history of life.
Technical basis and theoretical concepts
Relational database concepts of computer science and Information retrieval concepts of digital libraries are important for understanding biological databases. Biological database design, development, and long-term management is a core area of the discipline of bioinformatics. Data contents include gene sequences, textual descriptions, attributes and ontology classifications, citations, and tabular data. These are often described as semi-structured data, and can be represented as tables, key delimited records, and XML structures.
Access
Most biological databases are available through web sites that organise data such that users can browse through the data online. In addition the underlying data is usually available for download in a variety of formats. Biological data comes in many formats. These formats include text, sequence data, protein structure and links. Each of these can be found from certain sources, for example:
- Text formats are provided by PubMed and OMIM.
- Sequence data is provided by GenBank, in terms of DNA, and UniProt, in terms of protein.
- Protein structures are provided by PDB, SCOP, and CATH.
Problems and challenges
Biological knowledge is distributed among countless databases. This sometimes makes it difficult to ensure the consistency of information, e.g. when different names are used for the same species or different data formats. As a consequence, inter-operability is a constant challenge for information exchange. For instance, if a DNA sequence database stores the DNA sequence along the name of a species, a name change of that species may break the links to other databases which may use a different name. Integrative bioinformatics is one field attempting to tackle this problem by providing unified access. One solution is how biological databases cross-reference to other databases with accession numbers to link their related knowledge together (e.g. so that the accession number stays the same even if a species name changes). Redundancy is another problem, as many databases must store the same information, e.g. protein structure databases also contain the sequence of the proteins they cover, their sequence, and their bibliographic information.
Model-organism databases
Species-specific databases are available for some species, mainly those that are often used in research (model organisms). For example, EcoCyc is an E. coli database. Other popular model organism databases include Mouse Genome Informatics for the laboratory mouse, Mus musculus, the Rat Genome Database for Rattus, ZFIN for Danio Rerio (zebrafish), PomBase for the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, FlyBase for Drosophila, WormBase for the nematodes Caenorhabditis elegans and Caenorhabditis briggsae, and Xenbase for Xenopus tropicalis and Xenopus laevis frogs.
Biodiversity and species databases
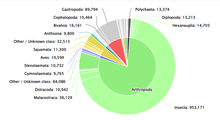
Numerous databases attempt to document the diversity of life on earth. A prominent example is the Catalogue of Life, first created in 2001 by Species 2000 and the Integrated Taxonomic Information System. The Catalogue of Life[1] is a collaborative project that aims to document taxonomic categorization of all currently accepted species in the world. The Catalogue of Life provides a consolidated and consistent database for researchers and policymakers to reference. The Catalogue of Life curates up-to-date datasets from other sources such as Conifer Database, ICTV MSL (for viruses), and LepIndex (for butterflies and moths). In total, the Catalogue of Life draws from 165 databases as of May 2022. Operational costs of the Catalogue of Life are paid for by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility, the Illinois Natural History Survey, the Naturalis Biodiversity Center, and the Smithsonian Institution.
Some biological databases also document geographical distribution of different species. Shuang Dai et al. created a new multi-source database to document spatial/geographical distribution of 1,371 bird species in China, as existing databases had been severely lacking in spatial distribution data for many species. Sources for this new database included books, literature, GPS tracking, and online webpage data. The new database displayed taxonomy, distribution, species info, and data sources for each species. After completion of the bird spatial distribution database, it was discovered that 61% of known species in China were found to be distributed in regions beyond where they were previously known.
Medical databases
Medical databases are a special case of biomedical data resource and can range from bibliographies, such as PubMed, to image databases for the development of AI based diagnostic software. For instance, one such image database was developed with the goal of aiding in the development of wound monitoring algorithms. Over 188 multi-modal image sets were curated from 79 patient visits, consisting of photographs, thermal images, and 3D mesh depth maps. Wound outlines were manually drawn and added to the photo datasets. The database was made publicly available in the form of a program called WoundsDB, downloadable from the Chronic Wound Database website. [2]
Nucleic Acids Research Database Issue
An important resource for finding biological databases is a special yearly issue of the journal Nucleic Acids Research (NAR). The Database Issue of NAR is freely available, and categorizes many of the public biological databases. A companion database to the issue called the Online Molecular Biology Database Collection lists 1,380 online databases. Other collections of databases exist such as MetaBase and the Bioinformatics Links Collection.
See also
- Biobank
- Biological data
- Chemical database
- Death Domain database
- European Bioinformatics Institute
- Gene Disease Database
- Integrative bioinformatics
- List of biological databases
- Model organism databases
- NCBI
- PubMed (a database of biomedical literature)
External links
- Interactive list of biological databases, classified by categories, from Nucleic Acids Research, 2010
- DBD: Database of Biological Databases
- Biosharing (a database of biological databases)
- Chronic Wounds Database WoundsDB
- Catalogue of Life Catalogue of Life
| Data collection | |
|---|---|
| Field concepts | |
| Applications | |
| Analysis techniques | |
| Major projects | |