
EVT-201
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
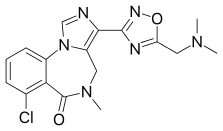
| Formula | C17H17ClN6O2 |
| Molar mass | 372.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
EVT-201 is a benzodiazepine derivative drug and partial positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. It has 2–4-fold higher functional affinity for the α1 subunit relative to the α2, α3, and α5 subunits and significantly less intrinsic activity in comparison to currently-marketed benzodiazepines and the Z-drugs. Despite the lower efficacy, EVT-201 still shows effectiveness in the treatment of insomnia, and it is thought that the lower efficacy may result in fewer side effects, such as motor incoordination. The drug was originally developed by Roche, based on preclinical data, as a non-sedating anxiolytic, but was found to produce sedation in humans in phase I clinical trials. For this reason, it was subsequently licensed to Evotec, which is now developing it for the treatment of insomnia. As of 2007, EVT-201 has completed phase II clinical trials for this indication, with positive findings reported. As of August 2015, Phase II development is ongoing in China.