
Eplerenone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /ɛpˈlɛrənoʊn/ |
| Trade names | Inspra, Epnone, Dosterep |
| Other names | SC-66110; CGP-30083; 9-11α-Epoxymexrenone; 9,11α-Epoxy-7α-methoxycarbonyl-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21,17-carbolactone |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a603004 |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth (tablets) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~70% |
| Protein binding | ~50% (33–60%) (primarily to α1-acid glycoprotein) |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4) |
| Metabolites | 6β-OH-EPL, 6β,21-OH-EPL, 21-OH-EPL, 3α,6β-OH-EPL (All inactive) |
| Elimination half-life | 4–6 hours |
| Excretion | Urine (67%), feces (32%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.106.615 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
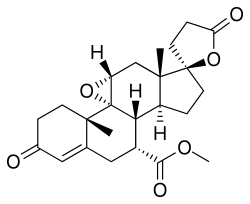
| Formula | C24H30O6 |
| Molar mass | 414.498 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Eplerenone, sold under the brand name Inspra, is an aldosterone antagonist type of potassium-sparing diuretic that is used to treat chronic heart failure and high blood pressure, particularly for patients with resistant hypertension due to elevated aldosterone. It is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group and a selective aldosterone receptor antagonist (SARA). Eplerenone is more selective than spironolactone at the mineralocorticoid receptor relative to binding at androgen, progestogen, glucocorticoid, or estrogen receptors.
Medical uses
Heart failure
Eplerenone reduces risk of death in patients with heart failure, particularly in patients with recent myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Hypertension
Eplerenone lowers blood pressure in patients with primary hypertension. Eplerenone also reduces arterial stiffness and vascular endothelial dysfunction.
For persons with resistant hypertension, eplerenone is safe and effective for reducing blood pressure, particularly in persons with resistant hypertension due to hyperaldosteronism.
Central serous chorioretinopathy
Eplerenone is often prescribed for people with central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC). However, the most recent and largest randomized controlled trial showed that eplerenone has no significant effect on chronic CSC that has been untreated for four months.
Adverse effects
Common adverse drug reactions (ADRs) associated with the use of eplerenone include: hyperkalaemia, hypotension, dizziness, and reduced renal clearance. Eplerenone may have a lower incidence than spironolactone of sexual side effects such as feminization, gynecomastia, impotence, low sex drive and reduction of size of male genitalia. This is because other antimineralocorticoids have structural elements of the progesterone molecule, causing progestogenic and antiandrogenic outcomes. When considering taking these medicines, it is important to note the variations in their ability to offset the nongenomic effects of aldosterone.
Currently, there is not enough evidence available from the randomized controlled trials on side effects of eplerenone to do a benefit versus risk assessment in people with primary hypertension.
Interactions
Eplerenone is primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP3A4. Thus the potential exists for adverse drug interactions with other drugs that induce or inhibit CYP3A4. Specifically, the concomitant use of the CYP3A4 potent inhibitors ketoconazole and itraconazole is contraindicated. Other CYP3A4 inhibitors including erythromycin, saquinavir, and verapamil should be used with caution. Other drugs that increase potassium concentrations may increase the risk of hyperkalemia associated with eplerenone therapy, including salt substitutes, potassium supplements and other potassium-sparing diuretics.
Pharmacology
Eplerenone is an antimineralocorticoid, or an antagonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR). Eplerenone is also known chemically as 9,11α-epoxy-7α-methoxycarbonyl-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-21,17-carbolactone and "was derived from spironolactone by the introduction of a 9α,11α-epoxy bridge and by substitution of the 17α-thoacetyl group of spironolactone with a carbomethoxy group." The drug controls high blood pressure by blocking the binding of aldosterone to the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) in epithelial tissues, such as the kidney. Blocking the action of aldosterone decreases blood volume and lowers blood pressure. It has 10- to 20-fold lower affinity for the MR relative to spironolactone, and is less potent in vivo as an antimineralocorticoid. However, in contrast to spironolactone, eplerenone has little affinity for the androgen, progesterone, and glucocorticoid receptors. It also has more consistently observed non-genomic antimineralocorticoid effects relative to spironolactone (see membrane mineralocorticoid receptor). Eplerenone differs from spironolactone in its extensive metabolism, with a short half-life and inactive metabolites.
Eplerenone seems to be about 50 to 75% as potent as spironolactone as an antimineralocorticoid. Hence, 25 mg/day spironolactone may be equivalent to approximately 50 mg/day eplerenone.
Regulatory and Patent History
Eplerenone was patented in 1983 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2002. Eplerenone is currently approved for sale in Canada, the US, EU, Netherlands and Japan. Eplerenone costs an estimated $2.93 per day when treating congestive heart failure and $5.86 per day when treating hypertension.
See also
|
Sulfonamides (and etacrynic acid) |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium-sparing (at CD) |
|
||||||||
| Osmotic diuretics (PT, DL) | |||||||||
|
Vasopressin receptor inhibitors (DCT and CD) |
|||||||||
| Other | |||||||||
| Combination products | |||||||||
| |||||||||
| Mineralocorticoids | |
|---|---|
| Antimineralocorticoids | |
| Synthesis modifiers | |
| |