
Life expectancy
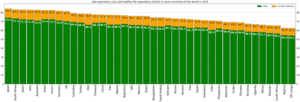
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the span of a life. It is sometimes used referring to inanimate objects, i.e. a building, but is generally used to estimate the average life span of living things, more specifically human life.
This average is calculated based on the year of birth, sex, and region, factoring in the causes of mortality that would most likely affect the particular population. As of 2016, the overall worldwide life expectancy had reached the highest level that has been measured in modern times.
The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth (LEB), which can be defined in two ways. Cohort LEB is the mean length of life of a birth cohort (in this case, all individuals born in a given year) and can be computed only for cohorts born so long ago that all their members have died. Period LEB is the mean length of life of a hypothetical cohort assumed to be exposed, from birth through death, to the mortality rates observed at a given year.
National LEB figures reported by national agencies and international organizations for human populations are estimates of period LEB. In the Bronze Age and the Iron Age, human LEB was 26 years; in 2010, world LEB was 67.2 years. In recent years, LEB in Eswatini (formerly Swaziland) is 49, while LEB in Japan is 83. The combination of high infant mortality and deaths in young adulthood from accidents, epidemics, plagues, wars, and childbirth, before modern medicine was widely available, significantly lowers LEB. For example, a society with a LEB of 40 would have relatively few people dying at exactly 40: most will die before 30 or after 55. In populations with high infant mortality rates, LEB is highly sensitive to the rate of death in the first few years of life. Because of this sensitivity, LEB can be grossly misinterpreted, leading to the belief that a population with a low LEB would have a small proportion of older people. A different measure, such as life expectancy at age 5 (e5), can be used to exclude the effect of infant mortality to provide a simple measure of overall mortality rates other than in early childhood. For instance, in a society with a life expectancy of 30, it may nevertheless be common to have a 40-year remaining timespan at age 5 (but perhaps not a 60-year one).
Until the middle of the 20th century, infant mortality was approximately 40–60% of the total mortality. Excluding child mortality, the average life expectancy during the 12th–19th centuries was approximately 55 years. If a person survived childhood, they had about a 50% chance of living 50–55 years, instead of only 25–40 years.
Aggregate population measures—such as the proportion of the population in various age groups—are also used alongside individual-based measures—such as formal life expectancy—when analyzing population structure and dynamics. Pre-modern societies had universally higher mortality rates and lower life expectancies at every age for both males and females. This example is relatively rare.
Life expectancy, longevity, and maximum lifespan are not synonymous. Longevity refers to the relatively long lifespan of some members of a population. Maximum lifespan is the age at death for the longest-lived individual of a species. Mathematically, life expectancy is denoted 

Life expectancy is also used in plant or animal ecology, and in life tables (also known as actuarial tables). The concept of life expectancy may also be used in the context of manufactured objects, though the related termshelf life is commonly used for consumer products, and the terms "mean time to breakdown" (MTTB) and "mean time between failures" (MTBF) are used in engineering.
Human patterns
Maximum
The longest verified lifespan for any human is that of Frenchwoman Jeanne Calment, who is verified as having lived to age 122 years, 164 days, between 21 February 1875 and 4 August 1997. This is referred to as the "maximum life span," which is the upper boundary of life, the maximum number of years any human is known to have lived. A theoretical study shows that the maximum life expectancy at birth is limited by the human life characteristic value δ, which is around 104 years. According to a study by biologists Bryan G. Hughes and Siegfried Hekimi, there is no evidence for limit on human lifespan. However, this view has been questioned on the basis of error patterns.
Records of human lifespan above age 100 are highly susceptible to errors. For example, the previous world-record holder for human lifespan, Carrie C. White was uncovered as a simple typographic error after more than two decades.
Variation over time
The following information is derived from the 1961 Encyclopædia Britannica and other sources, some with questionable accuracy. Unless otherwise stated, it represents estimates of the life expectancies of the world population as a whole. In many instances, life expectancy varied considerably according to class and gender.
Life expectancy at birth takes account of infant mortality and child mortality but not prenatal mortality.
| Era | Life expectancy at birth in years | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Paleolithic | 22–33 | Based on the data from modern hunter-gatherer populations, it is estimated that at 15, life expectancy was 54 years, with a 60% probability of reaching 15. |
| Neolithic | 20 – 33 | Based on Early Neolithic data, total life expectancy at 15 would be 28–33 years. |
| Bronze Age and Iron Age | 26 | Based on Early and Middle Bronze Age data, total life expectancy at 15 would be 28–36 years. |
| Classical Greece | 25 – 28 | Based on Athens Agora and Corinth data, total life expectancy at 15 would be 37–41 years. Most Greeks and Romans died young. About half of all children died before adolescence. Those who survived to the age of 30 had a reasonable chance of reaching 50 or 60. The truly elderly, however, were rare. Because so many died in childhood, life expectancy at birth was probably between 20 and 30 years. |
| Ancient Rome | 20–33 | Data is lacking, but computer models provide the estimate. If a person survived to age 20, they could expect to live around 30 years more. Life expectancy was probably slightly longer for women than men. When infant mortality is factored out (i.e. counting only the 67–75% who survived the first year), life expectancy is around 34–41 more years (i.e. expected to live to 35–42). When child mortality is factored out (i.e. counting only the 55-65% who survived to age 5), life expectancy is around 40–45 (i.e. age 45–50). The ~50% that reached age 10 could also expect to reach ~45-50; at 15 to ~48–54; at 40 to ~60; at 50 to ~64–68; at 60 to ~70–72; at 70 to ~76–77. |
| Wang clan of China, 1st c. AD – 1749 | 35 | For the 60% that survived the first year (i.e. excluding infant mortalities), life expectancy rose to ~35. |
| Early Middle Ages (Europe, from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century) | 30–35 | Life expectancy for those of both sexes who survived birth averaged about 30–35 years. However, if a Gaulish boy made it past age 20, he might expect to live 25 more years, while a woman at age 20 could normally expect about 17 more years. Anyone who survived until 40 had a good chance at another 15 to 20 years. |
| Pre-Columbian Mesoamerica | >40 | The average Aztec life expectancy was 41.2 years for men and 42.1 for women. |
| Late medieval English peerage | 30–33 | In Europe, around one-third of infants died in their first year. Once children reached the age of 10, their life expectancy was 32.2 years, and for those who survived to 25, the remaining life expectancy was 23.3 years. Such estimates reflected the life expectancy of adult males from the higher ranks of English society in the Middle Ages, and were similar to that computed for monks of the Christ Church in Canterbury during the 15th century. At age 21, life expectancy of an aristocrat was an additional 43 years (total age 64). |
| Early modern Britain (16th – 18th century) | 33–40 | For males in the 18th century it was 34 years. For 15-year-old girls: around the 15th – 16th century it was ~33 years (48 total), and in the 18th century it was ~42 (57 total). |
| 18th-century England | 25–40 | For most of the century it ranged from 35 to 40; however, in the 1720s it dipped as low as 25. For 15-year-old girls, it was ~42 (57 total). During the second half of the century it was ~37, while for the elite it passed 40 and approached 50. |
| Pre-Champlain Canadian Maritimes | 60 | Samuel de Champlain wrote that in his visits to Mi'kmaq and Huron communities, he met people over 100 years old. Daniel Paul attributes the incredible lifespan in the region to low stress and a healthy diet of lean meats, diverse vegetables, and legumes. |
| 18th-century Prussia | 24.7 | For males. |
| 18th-century France | 27.5–30 | For males: 24.8 years in 1740–1749, 27.9 years in 1750–1759, 33.9 years in 1800–1809. |
| 18th-century American colonies | 28 | Massachusetts colonists who reached the age of 50 could expect to live until 71, and those who were still alive at 60 could expect to reach 75. |
| Beginning of the 19th century | ~29 | Demographic research suggests that at the beginning of the 19th century, no country in the world had a life expectancy longer than 40 years. India was ~25 years, while Belgium was ~40 years. For Europe as a whole, it was ~33 years. |
| Early 19th-century England | 40 | For the 84% who survived the first year (i.e. excluding infant mortality), the average age was ~46–48. If they reached 20, then it was ~60; if 50, then ~70; if 70, then ~80. For a 15-year-old girl it was ~60–65. For the upper-class, LEB rose from ~45 to 50. Less than half of the people born in the mid-19th century made it past their 50th birthday. In contrast, 97% of the people born in 21st century England and Wales can expect to live longer than 50 years. |
| 19th-century British India | 25.4 | |
| 19th-century world average | 28.5–32 | Over the course of the century: Europe rose from ~33 to 43, the Americas from ~35 to 41, Oceania ~35 to 48, Asia ~28, Africa 26. In 1820s France, LEB was ~38, and for the 80% that survived, it rose to ~47. For Moscow serfs, LEB was ~34, and for the 66% that survived, it rose to ~36. Western Europe in 1830 was ~33 years, while for the people of Hau-Lou in China, it was ~40. The LEB for a 10-year-old in Sweden rose from ~44 to ~54. |
| 1900 world average | 31–32 | Around 48 years in Oceania, 43 in Europe, and 41 in the Americas. Around 47 in the U.S. and around 48 for 15-year-old girls in England. |
| 1950 world average | 45.7–48 | Around 60 years in Europe, North America, Oceania, Japan, and parts of South America; but only 41 in Asia and 36 in Africa. Norway led with 72, while in Mali it was merely 26. |
| 2019–2020 world average | 72.6–73.2 |
|
Life expectancy increases with age as the individual survives the higher mortality rates associated with childhood. For instance, the table above gives the life expectancy at birth among 13th-century English nobles at 30. Having survived to the age of 21, a male member of the English aristocracy in this period could expect to live:
- 1200–1300: to age 64
- 1300–1400: to age 45 (because of the bubonic plague)
- 1400–1500: to age 69
- 1500–1550: to age 71
17th-century English life expectancy was only about 35 years, largely because infant and child mortality remained high. Life expectancy was under 25 years in the early Colony of Virginia, and in seventeenth-century New England, about 40% died before reaching adulthood. During the Industrial Revolution, the life expectancy of children increased dramatically. The under-5 mortality rate in London decreased from 74.5% (in 1730–1749) to 31.8% (in 1810–1829).
Public health measures are credited with much of the recent increase in life expectancy. During the 20th century, despite a brief drop due to the 1918 flu pandemic, the average lifespan in the United States increased by more than 30 years, of which 25 years can be attributed to advances in public health.
Regional variations
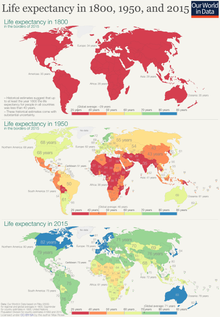
Human beings are expected to live on average 30–40 years in Eswatini and 82.6 years in Japan. An analysis published in 2011 in The Lancet attributes Japanese life expectancy to equal opportunities, public health, and diet.

There are great variations in life expectancy between different parts of the world, mostly caused by differences in public health, medical care, and diet. The impact of AIDS on life expectancy is particularly notable in many African countries. According to projections made by the United Nations in 2002, the life expectancy at birth for 2010–2015 (if HIV/AIDS did not exist) would have been:
- 70.7 years instead of 31.6 years, Botswana
- 69.9 years instead of 41.5 years, South Africa
- 70.5 years instead of 31.8 years, Zimbabwe
Actual life expectancy in Botswana declined from 65 in 1990 to 49 in 2000 before increasing to 66 in 2011. In South Africa, life expectancy was 63 in 1990, 57 in 2000, and 58 in 2011. And in Zimbabwe, life expectancy was 60 in 1990, 43 in 2000, and 54 in 2011.
During the last 200 years, African countries have generally not had the same improvements in mortality rates that have been enjoyed by countries in Asia, Latin America, and Europe.
In the United States, African-American people have shorter life expectancies than their European-American counterparts. For example, white Americans in 2010 are expected to live until age 78.9, but black Americans only until age 75.1. This 3.8-year gap, however, is the lowest it has been since 1975 at the latest. The greatest difference was 7.1 years in 1993. In contrast, Asian-American women live the longest of all ethnic groups in the United States, with a life expectancy of 85.8 years. The life expectancy of Hispanic-Americans is 81.2 years. According to the new government reports in the US, life expectancy in the country dropped again because of the rise in suicide and drug overdose rates. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) found nearly 70,000 more Americans died in 2017 than in 2016, with rising rates of death among 25- to 44-year-olds.
Cities also experience a wide range of life expectancy based on neighborhood breakdowns. This is largely due to economic clustering and poverty conditions that tend to associate based on geographic location. Multi-generational poverty found in struggling neighborhoods also contributes. In United States cities such as Cincinnati, the life expectancy gap between low income and high-income neighborhoods touches 20 years.
Economic circumstances

Economic circumstances also affect life expectancy. For example, in the United Kingdom, life expectancy in the wealthiest and richest areas is several years higher than in the poorest areas. This may reflect factors such as diet and lifestyle, as well as access to medical care. It may also reflect a selective effect: people with chronic life-threatening illnesses are less likely to become wealthy or to reside in affluent areas. In Glasgow, the disparity is amongst the highest in the world: life expectancy for males in the heavily deprived Calton area stands at 54, which is 28 years less than in the affluent area of Lenzie, which is only 8 km (5.0 mi) away.
A 2013 study found a pronounced relationship between economic inequality and life expectancy. However, in contrast, a study by José A. Tapia Granados and Ana Diez Roux at the University of Michigan found that life expectancy actually increased during the Great Depression, and during recessions and depressions in general. The authors suggest that when people are working at a more extreme degree during prosperous economic times, they undergo more stress, exposure to pollution, and the likelihood of injury among other longevity-limiting factors.
Life expectancy is also likely to be affected by exposure to high levels of highway air pollution or industrial air pollution. This is one way that occupation can have a major effect on life expectancy. Coal miners (and in prior generations, asbestos cutters) often have lower life expectancies than average. Other factors affecting an individual's life expectancy are genetic disorders, drug use, tobacco smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, access to health care, diet, and exercise.
Sex differences

In the present, female human life expectancy is greater than that of males, despite females having higher morbidity rates (see Health survival paradox). There are many potential reasons for this. Traditional arguments tend to favor sociology-environmental factors: historically, men have generally consumed more tobacco, alcohol, and drugs than women in most societies, and are more likely to die from many associated diseases such as lung cancer, tuberculosis, and cirrhosis of the liver. Men are also more likely to die from injuries, whether unintentional (such as occupational, war, or car wrecks) or intentional (suicide). Men are also more likely to die from most of the leading causes of death (some already stated above) than women. Some of these in the United States include cancer of the respiratory system, motor vehicle accidents, suicide, cirrhosis of the liver, emphysema, prostate cancer, and coronary heart disease. These far outweigh the female mortality rate from breast cancer and cervical cancer. In the past, mortality rates for females in child-bearing age groups were higher than for males at the same age.
A paper from 2015 found that female foetuses have a higher mortality rate than male foetuses. This finding contradicts papers dating from 2002 and earlier that attribute the male sex to higher in-utero mortality rates. Among the smallest premature babies (those under 2 pounds (910 grams)), females have a higher survival rate. At the other extreme, about 90% of individuals aged 110 are female. The difference in life expectancy between men and women in the United States dropped from 7.8 years in 1979 to 5.3 years in 2005, with women expected to live to age 80.1 in 2005. Data from the United Kingdom shows the gap in life expectancy between men and women decreasing in later life. This may be attributable to the effects of infant mortality and young adult death rates.
Some argue that shorter male life expectancy is merely another manifestation of the general rule, seen in all mammal species, that larger-sized individuals within a species tend, on average, to have shorter lives. This biological difference occurs because women have more resistance to infections and degenerative diseases.
In her extensive review of the existing literature, Kalben concluded that the fact that women live longer than men was observed at least as far back as 1750 and that, with relatively equal treatment, today males in all parts of the world experience greater mortality than females. However, Kalben's study was restricted to data in Western Europe alone, where the demographic transition occurred relatively early. United Nations statistics from mid-twentieth century onward, show that in all parts of the world, females have a higher life expectancy at age 60 than males. Of 72 selected causes of death, only 6 yielded greater female than male age-adjusted death rates in 1998 in the United States. Except for birds, for almost all of the animal species studied, males have higher mortality than females. Evidence suggests that the sex mortality differential in people is due to both biological/genetic and environmental/behavioral risk and protective factors.
One recent suggestion is that mitochondrial mutations which shorten lifespan continue to be expressed in males (but less so in females) because mitochondria are inherited only through the mother. By contrast, natural selection weeds out mitochondria that reduce female survival; therefore, such mitochondria are less likely to be passed on to the next generation. This thus suggests that females tend to live longer than males. The authors claim that this is a partial explanation.
Another explanation is the unguarded X hypothesis. According to this hypothesis, one reason for why the average lifespan of males isn't as long as that of females––by 18% on average, according to the study––is that they have a Y chromosome which can't protect an individual from harmful genes expressed on the X chromosome, while a duplicate X chromosome, as present in female organisms, can ensure harmful genes aren't expressed.
Before the Industrial Revolution, men lived longer than women on average. In developed countries, starting around 1880, death rates decreased faster among women, leading to differences in mortality rates between males and females. Before 1880, death rates were the same. In people born after 1900, the death rate of 50- to 70-year-old men was double that of women of the same age. Men may be more vulnerable to cardiovascular disease than women, but this susceptibility was evident only after deaths from other causes, such as infections, started to decline. Most of the difference in life expectancy between the sexes is accounted for by differences in the rate of death by cardiovascular diseases among persons aged 50–70.
Genetics
The heritability of lifespan is estimated to be less than 10%, meaning the majority of variation in lifespan is attributable due to differences in environment rather than genetic variation. However, researchers have identified regions of the genome which can influence the length of life and the number of years lived in good health. For example, a genome-wide association study of 1 million lifespans found 12 genetic loci which influenced lifespan by modifying susceptibility to cardiovascular and smoking-related disease. The locus with the largest effect is APOE. Carriers of the APOE ε4 allele live approximately one year less than average (per copy of the ε4 allele), mainly due to increased risk of Alzheimer's disease.
In July 2020, scientists identified 10 genomic loci with consistent effects across multiple lifespan-related traits, including healthspan, lifespan, and longevity. The genes affected by variation in these loci highlighted haem metabolism as a promising candidate for further research within the field. This study suggests that high levels of iron in the blood likely reduce, and genes involved in metabolising iron likely increase healthy years of life in humans.
A follow-up study which investigated the genetics of frailty and self-rated health in addition to healthspan, lifespan, and longevity also highlighted haem metabolism as an important pathway, and found genetic variants which lower blood protein levels of LPA and VCAM1 were associated with increased healthy lifespan.
Centenarians
In developed countries, the number of centenarians is increasing at approximately 5.5% per year, which means doubling the centenarian population every 13 years, pushing it from some 455,000 in 2009 to 4.1 million in 2050. Japan is the country with the highest ratio of centenarians (347 for every 1 million inhabitants in September 2010). Shimane Prefecture had an estimated 743 centenarians per million inhabitants.
In the United States, the number of centenarians grew from 32,194 in 1980 to 71,944 in November 2010 (232 centenarians per million inhabitants).
Mental illness
Mental illness is reported to occur in approximately 18% of the average American population.
The mentally ill have been shown to have a 10- to 25-year reduction in life expectancy. Generally, the reduction of lifespan in the mentally ill population compared to the mentally stable population has been studied and documented.
The greater mortality of people with mental disorders may be due to death from injury, from co-morbid conditions, or medication side effects. For instance, psychiatric medications can increase the risk of developing diabetes. It has been shown that the psychiatric medication olanzapine can increase risk of developing agranulocytosis, among other comorbidities. Psychiatric medicines also affect the gastrointestinal tract; the mentally ill have a four times risk of gastrointestinal disease.
As of 2020 and the COVID-19 pandemic, researchers have found an increased risk of death in the mentally ill.
Other illnesses
The life expectancy of people with diabetes, which is 9.3% of the U.S. population, is reduced by roughly 10–20 years. People over 60 years old with Alzheimer's disease have about a 50% life expectancy of 3–10 years. Other demographics that tend to have a lower life expectancy than average include transplant recipients and the obese.
Education
Education on all levels has been shown to be strongly associated with increased life expectancy. This association may be due partly to higher income, which can lead to increased life expectancy. Despite the association, among identical twin pairs with different education levels, there is only weak evidence of a relationship between educational attainment and adult mortality.
According to a paper from 2015, the mortality rate for the Caucasian population in the United States from 1993 to 2001 is four times higher for those who did not complete high school compared to those who have at least 16 years of education. In fact, within the U.S. adult population, people with less than a high school education have the shortest life expectancies.
Preschool education also plays a large role in life expectancy. It was found that high-quality early-stage childhood education had positive effects on health. Researchers discovered this by analyzing the results of the Carolina Abecedarian Project, finding that the disadvantaged children who were randomly assigned to treatment had lower instances of risk factors for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases in their mid-30s.
Evolution and aging rate
Various species of plants and animals, including humans, have different lifespans. Evolutionary theory states that organisms which—by virtue of their defenses or lifestyle—live for long periods and avoid accidents, disease, predation, etc. are likely to have genes that code for slow aging, which often translates to good cellular repair. One theory is that if predation or accidental deaths prevent most individuals from living to an old age, there will be less natural selection to increase the intrinsic life span. That finding was supported in a classic study of opossums by Austad; however, the opposite relationship was found in an equally prominent study of guppies by Reznick.
One prominent and very popular theory states that lifespan can be lengthened by a tight budget for food energy called caloric restriction. Caloric restriction observed in many animals (most notably mice and rats) shows a near doubling of life span from a very limited calorific intake. Support for the theory has been bolstered by several new studies linking lower basal metabolic rate to increased life expectancy. That is the key to why animals like giant tortoises can live so long. Studies of humans with life spans of at least 100 have shown a link to decreased thyroid activity, resulting in their lowered metabolic rate.
In a broad survey of zoo animals, no relationship was found between investment of the animal in reproduction and its life span.
Calculation
In actuarial notation, the probability of surviving from age 






-
()
The curtate future lifetime, denoted 




-
()
Substituting (1) into the sum and simplifying gives the final result
-
()
If the assumption is made that, on average, people live a half year on the year of their death, the complete life expectancy at age 

By definition, life expectancy is an arithmetic mean. It can also be calculated by integrating the survival curve from 0 to positive infinity (or equivalently to the maximum lifespan, sometimes called 'omega'). For an extinct or completed cohort (all people born in the year 1850, for example), it can of course simply be calculated by averaging the ages at death. For cohorts with some survivors, it is estimated by using mortality experience in recent years. The estimates are called period cohort life expectancies.
The starting point for calculating life expectancy is the age-specific death rates of the population members. If a large amount of data is available, a statistical population can be created that allow the age-specific death rates to be simply taken as the mortality rates actually experienced at each age (the number of deaths divided by the number of years "exposed to risk" in each data cell). However, it is customary to apply smoothing to remove (as much as possible) the random statistical fluctuations from one year of age to the next. In the past, a very simple model used for this purpose was the Gompertz function, but more sophisticated methods are now used. The most common modern methods include:
- fitting a mathematical formula (such as the Gompertz function, or an extension of it) to the data.
- looking at an established mortality table derived from a larger population and making a simple adjustment to it (such as multiplying by a constant factor) to fit the data. (In cases of relatively small amounts of data.)
- looking at the mortality rates actually experienced at each age and applying a piecewise model (such as by cubic splines) to fit the data. (In cases of relatively large amounts of data.)
The age-specific death rates are calculated separately for separate groups of data that are believed to have different mortality rates (such as males and females, or smokers and non-smokers) and are then used to calculate a life table from which one can calculate the probability of surviving to each age. While the data required are easily identified in the case of humans, the computation of life expectancy of industrial products and wild animals involves more indirect techniques. The life expectancy and demography of wild animals are often estimated by capturing, marking, and recapturing them. The life of a product, more often termed shelf life, is also computed using similar methods. In the case of long-lived components, such as those used in critical applications (e.g. aircraft), methods like accelerated aging are used to model the life expectancy of a component.
It is important to note that the life expectancy statistic is usually based on past mortality experience and assumes that the same age-specific mortality rates will continue. Thus, such life expectancy figures need to be adjusted for temporal trends before calculating how long a currently living individual of a particular age is expected to live. Period life expectancy remains a commonly used statistic to summarize the current health status of a population. However, for some purposes, such as pensions calculations, it is usual to adjust the life table used by assuming that age-specific death rates will continue to decrease over the years, as they have usually done in the past. That is often done by simply extrapolating past trends, but some models exist to account for the evolution of mortality, like the Lee–Carter model.
As discussed above, on an individual basis, some factors correlate with longer life. Factors that are associated with variations in life expectancy include family history, marital status, economic status, physique, exercise, diet, drug use (including smoking and alcohol consumption), disposition, education, environment, sleep, climate, and health care.
Healthy life expectancy
To assess the quality of these additional years of life, 'healthy life expectancy' has been calculated for the last 30 years. Since 2001, the World Health Organization has published statistics called Healthy life expectancy (HALE), defined as the average number of years that a person can expect to live in "full health" excluding the years lived in less than full health due to disease and/or injury. Since 2004, Eurostat publishes annual statistics called Healthy Life Years (HLY) based on reported activity limitations. The United States uses similar indicators in the framework of the national health promotion and disease prevention plan "Healthy People 2010". More and more countries are using health expectancy indicators to monitor the health of their population.
The long-standing quest for longer life led in the 2010s to a more promising focus on increasing HALE, also known as a person's "healthspan". Besides the benefits of keeping people healthier longer, a goal is to reduce health-care expenses on the many diseases associated with cellular senescence. Approaches being explored include fasting, exercise, and senolytic drugs.
Forecasting
Forecasting life expectancy and mortality form an important subdivision of demography. Future trends in life expectancy have huge implications for old-age support programs (like U.S. Social Security and pension) since the cash flow in these systems depends on the number of recipients who are still living (along with the rate of return on the investments or the tax rate in pay-as-you-go systems). With longer life expectancies, the systems see increased cash outflow; if the systems underestimate increases in life-expectancies, they will be unprepared for the large payments that will occur, as humans live longer and longer.
Life expectancy forecasting is usually based on one of two different approaches:
- Forecasting the life expectancy directly, generally using ARIMA or other time-series extrapolation procedures. This has the advantage of simplicity, but it cannot account for changes in mortality at specific ages, and the forecast number cannot be used to derive other life table results. Analyses and forecasts using this approach can be done with any common statistical/mathematical software package, like EViews, R, SAS, Stata, Matlab, or SPSS.
- Forecasting age-specific death rates and computing the life expectancy from the results with life table methods. This is usually more complex than simply forecasting life expectancy because the analyst must deal with correlated age-specific mortality rates, but it seems to be more robust than simple one-dimensional time series approaches. It also yields a set of age-specific rates that may be used to derive other measures, such as survival curves or life expectancies at different ages. The most important approach in this group is the Lee-Carter model, which uses the singular value decomposition on a set of transformed age-specific mortality rates to reduce their dimensionality to a single time series, forecasts that time series, and then recovers a full set of age-specific mortality rates from that forecasted value. The software includes Professor Rob J. Hyndman's R package called 'demography' and UC Berkeley's LCFIT system.
Policy uses
Life expectancy is one of the factors in measuring the Human Development Index (HDI) of each nation along with adult literacy, education, and standard of living.
Life expectancy is used in describing the physical quality of life of an area. It is also used for an individual when the value of a life settlement is determined a life insurance policy is sold for a cash asset.
Disparities in life expectancy are often cited as demonstrating the need for better medical care or increased social support. A strongly associated indirect measure is income inequality. For the top 21 industrialized countries, if each person is counted equally, life expectancy is lower in more unequal countries (r = −0.907). There is a similar relationship among states in the U.S. (r = −0.620).
Life expectancy vs. other measures of longevity
Life expectancy is commonly confused with the average age an adult could expect to live. This confusion may create the expectation that an adult would be unlikely to exceed an average life expectancy, even though, with all statistical probability, an adult, who has already avoided many statistical causes of adolescent mortality, should be expected to outlive the average life expectancy calculated from birth. One must compare the life expectancy of the period after childhood to estimate also the life expectancy of an adult.
Life expectancy can change dramatically after childhood. In the table above, note the life expectancy at birth in the Paleolithic is 22-33 years, but life expectancy at 15 is 54 years. Additional studies similarly show a dramatic increase in life expectancy once adulthood was reached.
Maximum life span is an individual-specific concept, and therefore is an upper bound rather than an average. Science author Christopher Wanjek writes, "[H]as the human race increased its life span? Not at all. This is one of the biggest misconceptions about old age: we are not living any longer." The maximum life span, or oldest age a human can live, may be constant. Further, there are many examples of people living significantly longer than the average life expectancy of their time period, such as Socrates (71), Saint Anthony the Great (105), Michelangelo (88), and John Adams (90).
However, anthropologist John D. Hawks criticizes the popular conflation of life span (life expectancy) and maximum life span when popular science writers falsely imply that the average adult human does not live longer than their ancestors. He writes, "[a]ge-specific mortality rates have declined across the adult lifespan. A smaller fraction of adults die at 20, at 30, at 40, at 50, and so on across the lifespan. As a result, we live longer on average... In every way we can measure, human lifespans are longer today than in the immediate past, and longer today than they were 2000 years ago... age-specific mortality rates in adults really have reduced substantially."
Life expectancy can also create popular misconceptions about at what age a certain population may expect to die at. The modal age at death is the age when most deaths occur in a population, and is sometimes used instead of life expectancy for this kind of understanding. For example, in the table above, life expectancy in the Paleolithic is listed as 22-33 years. For many, this implies that most people in the Paleolithic died in their late twenties. However, in the Paleolithic, most adults in the Paleolithic died at 72 years (the average modal adult life span).
See also
- Biodemography
- Calorie restriction
- Demography
- Depreciation
- DNA damage theory of aging
- Glasgow effect
- Health equity
- Life extension
- Life table
- Lindy effect
- List of countries by life expectancy
- List of countries by past life expectancy
- List of longest-living organisms
- Maximum life span
- Medieval demography
- Mitohormesis
- Mortality rate
- Population pyramid
- Senescence
Increasing life expectancy
Further reading
- Leonid A. Gavrilov & Natalia S. Gavrilova (1991), The Biology of Life Span: A Quantitative Approach. New York: Harwood Academic Publisher, ISBN 3-7186-4983-7.
- Kochanek, Kenneth D., Elizabeth Arias, and Robert N. Anderson (2013), How Did Cause of Death Contribute to Racial Differences in Life Expectancy in the United States in 2010?. Hyattsville, Md.: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
External links
- Charts for all countries
- Our World In Data – Life Expectancy—Visualizations of how life expectancy around the world has changed historically (by Max Roser). Includes life expectancy for different age groups. Charts for all countries, world maps, and links to more data sources.
- Global Agewatch has the latest internationally comparable statistics on life expectancy from 195 countries.
- Rank Order—Life expectancy at birth Archived December 29, 2018, at the Wayback Machine from the CIA's World Factbook.
- Annual Life Tables since 1966; Decennial Life Tables since 1890 from the US Centers for Disease Controls and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics.
- Life expectancy in Roman times from the University of Texas.
- Animal lifespans: Animal Lifespans from Tesarta Online (Internet Archive); The Life Span of Animals from Dr. Bob's All Creatures Site.
| Ageing | |
|---|---|
| Life extension | |
| Immortality | |
| Records | |
| Longevity genes | |
| Related | |









![{\displaystyle e_{x}=\operatorname {E} [K(x)]=\sum _{k=0}^{\infty }k\,\cdot \Pr(K(x)=k)=\sum _{k=0}^{\infty }k\,\,_{k}p_{x}\,\,q_{x+k}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f479ebacfef15f4f97a64835040193d57f7d9a0f)
