
List of arylcyclohexylamines
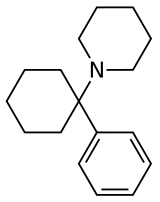
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs.
History
Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has been expanded by scientific research into stimulant, analgesic, and neuroprotective agents, and also by clandestine chemists in search of novel recreational drugs.
Structure
An arylcyclohexylamine is composed of a cyclohexylamine unit with an aryl moiety attachment. The aryl group is positioned geminal to the amine. In the simplest cases, the aryl moiety is typically a phenyl ring, sometimes with additional substitution. The amine is usually not primary; secondary amines such as methylamine or ethylamine, or tertiary cycloalkylamines such as piperidine and pyrrolidine, are the most commonly encountered N-substituents.
Pharmacology
Arylcyclohexylamines varyingly possess NMDA receptor antagonistic,dopamine reuptake inhibitory, and μ-opioid receptor agonistic properties. Additionally, σ receptor agonistic,nACh receptor antagonistic, and D2 receptor agonistic actions have been reported for some of these agents. Antagonism of the NMDA receptor confers anesthetic, anticonvulsant, neuroprotective, and dissociative effects; blockade of the dopamine transporter mediates stimulant and euphoriant effects as well as psychosis in high amounts; and activation of the μ-opioid receptor causes analgesic and euphoriant effects. Stimulation of the σ and D2 receptors may also contribute to hallucinogenic and psychotomimetic effects.
These are versatile agents with a wide range of possible pharmacological activities depending on the extent and range to which chemical modifications are implemented. The various choice of substitutions that are made allows for "fine-tuning" of the pharmacological profile that results. As examples, BTCP is a selective dopamine reuptake inhibitor, PCP is primarily an NMDA antagonist, and BDPC is a potent μ-opioid agonist, while PRE-084 is a selective sigma receptor agonist. Thus, radically different pharmacology is possible through different structural combinations.
PCP itself is composed of three six-membered rings, which can each be substituted by a variety of groups. These are traditionally numbered in the older research as first the cyclohexyl ring, then the phenyl, and finally the piperidine ring, with the different rings represented by prime notation (') next to the number. For instance, 4-methyl-PCP, 4'-methyl-PCP and 4''-methyl-PCP are all known compounds, with similar activity but quite different potencies.
However, since the widespread sale of these compounds as grey-market designer drugs, nearly all such compounds that have come to prominence either have a bare cyclohexyl ring or a 2-ketocyclohexyl ring, while the piperidine is replaced by a variety of alkyl or cycloalkyl amines and most substitution has taken place on the phenyl ring. Consequently it is common for widely used phenyl substituted analogues such as 3'-MeO-PCP and 3'-MeO-PCE to be referred to as 3-MeO-PCP and 3-MeO-PCE without the prime, even though this is technically incorrect and could lead to confusion.
List of arylcyclohexylamines
| Structures | Compound | Aryl Substituent | N Group | Cyclohexyl ring | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
PCA | Phenyl | NH2 | - | 1934-71-0 |
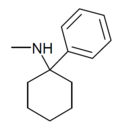 |
PCM | Phenyl | Methylamino | - | 2201-16-3 |
 |
Eticyclidine | Phenyl | Ethylamino | - | 2201-15-2 |
 |
PCPr | Phenyl | n-Propylamino | - | 18949-81-0 |
 |
PCiP | Phenyl | Isopropylamino | - | 1195-42-2 |
 |
PCAL | Phenyl | Allylamino | - | 2185-95-7 |
 |
PCBu | Phenyl | n-Butylamino | - | 73166-29-7 |
 |
PCEOH | Phenyl | Hydroxyethylamino | - | 2201-22-1 |
 |
PCMEA | Phenyl | Methoxyethylamino | - | 2201-57-2 |
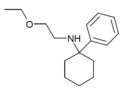 |
PCEEA | Phenyl | Ethoxyethylamino | - | 1072895-05-6 |
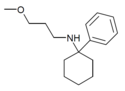 |
PCMPA | Phenyl | Methoxypropylamino | - | 2201-58-3 |
 |
PCDM | Phenyl | Dimethylamino | - | 2201-17-4 |
 |
Dieticyclidine | Phenyl | Diethylamino | - | 2201-19-6 |
 |
2-HO-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Hydroxy | 94852-58-1 |
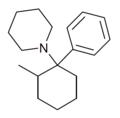 |
2-Me-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Methyl | 59397-29-4 |
 |
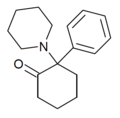
2-MeO-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Methoxy | 78636-34-7 |
 |
2-Keto-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 2-Keto | 101688-16-8 |
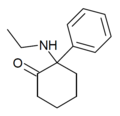 |
Eticyclidone ("O-PCE") | Phenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 6740-82-5 |
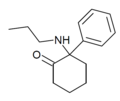 |
2-Keto-PCPr | Phenyl | n-Propylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
4-Methyl-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 4-Methyl | 19420-52-1 |
 |
4-Keto-PCP | Phenyl | Piperidine | 4-Keto | 65620-13-5 |
 |
2'-Cl-PCP | o-Chlorophenyl | Piperidine | - | 2201-31-2 |
 |
3'-Cl-PCP | m-Chlorophenyl | Piperidine | - | 2201-32-3 |
 |
2'-MeO-PCP | o-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | 2201-34-5 |
 |
3'-F-PCP | m-Fluorophenyl | Piperidine | - | 89156-99-0 |
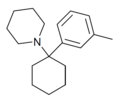 |
3'-Me-PCP | m-Tolyl | Piperidine | - | 2201-30-1 |
 |
3'-Me-PCPy | m-Tolyl | Pyrrolidine | - | 1622348-63-3 |
 |
3'-NH2-PCP | m-Aminophenyl | Piperidine | - | 72242-00-3 |
 |
3'-HO-PCP | m-Hydroxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | 79787-43-2 |
 |
3'-MeO-PCP | m-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | 72242-03-6 |
 |
3',4'-MD-PCP | 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | |
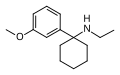 |
3'-MeO-PCE | m-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | - | 1364933-80-1 |
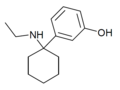 |
3'-HO-PCE | m-Hydroxyphenyl | Ethylamino | - | |
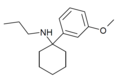 |
3'-MeO-PCPr | m-Methoxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | - | 1364933-81-2 |
 |
3'-HO-PCPr | m-Hydroxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | - | |
 |
3',4'-MD-PCPr | 3,4-Methylenedioxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | - | |
 |
3'-MeO-PCPy | m-Methoxyphenyl | Pyrrolidine | - | 1364933-79-8 |
 |
4'-HO-PCP | p-Hydroxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | 66568-88-5 |
 |
Methoxydine (4'-MeO-PCP) | p-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | - | 2201-35-6 |
 |
4'-MeO-PCE | p-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | - | |
 |
4'-F-PCP | p-Fluorophenyl | Piperidine | - | 22904-99-0 |
 |
4'-F-PCPy | p-Fluorophenyl | Pyrrolidine | - | |
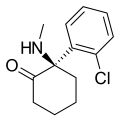 |
Arketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 33643-49-1 |
 |
Deschloroketamine | Phenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 7063-30-1 |
 |
Esketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 33643-46-8 |
 |
Ketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 6740-88-1 |
 |
Hydroxynorketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | NH2 | 2-Keto, 6-Hydroxy | 81395-70-2 |
 |
Ethketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 1354634-10-8 |
 |
NPNK | o-Chlorophenyl | n-Propylamino | 2-Keto | 2749326-65-4 |
 |
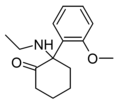
Methoxyketamine | o-Methoxyphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 7063-51-6 |
 |
2-MeO-NEK | o-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | |
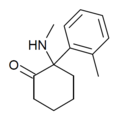 |
oMDCK | o-Tolyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 7063-37-8 |
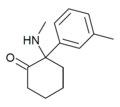 |
mMDCK | m-Tolyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
meta-Ketamine | m-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 7063-53-8 |
 |
iso-Ketamine | o-Chlorophenyl | Methylamino | 4-Keto | |
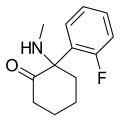 |
2-Fluorodeschloroketamine | o-Fluorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 111982-50-4 |
 |
3-Fluorodeschloroketamine | m-Fluorophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 2657761-23-2 |
 |
Bromoketamine | o-Bromophenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 120807-70-7 |
 |
TFMDCK | o-Trifluoromethylphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 1782149-73-8 |
 |
SN 35210 | o-Chlorophenyl | Carbomethoxybutylamino | 2-Keto | 1450615-41-4 |
 |
Methoxetamine | m-Methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 1239943-76-0 |
 |
Methoxmetamine | m-Methoxyphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | 1781829-56-8 |
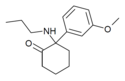 |
Methoxpropamine | m-Methoxyphenyl | n-Propylamino | 2-Keto | 2504100-71-2 |
 |
MXiPr | m-Methoxyphenyl | i-Propylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
Ethoxetamine | m-Ethoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
Deoxymethoxetamine (3-Me-2'-Oxo-PCE) | m-Tolyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 2666932-45-0 |
 |
Br-MXE | 2-bromo-5-methoxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
Hydroxetamine (HXE) | m-Hydroxyphenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 1620054-73-0 |
 |
HXM | m-Hydroxyphenyl | Methylamino | 2-Keto | |
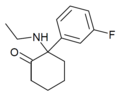 |
Fluorexetamine (FXE) | m-Fluorophenyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
Phencyclidine (PCP) | Phenyl | Piperidine | - | 77-10-1 |
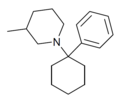 |
PC3MP | Phenyl | 3-Methylpiperidine | - | 2201-41-4 |
 |
PC4MP | Phenyl | 4-Methylpiperidine | - | 2201-42-5 |
 |
Rolicyclidine (PCPy) | Phenyl | Pyrrolidine | - | 2201-39-0 |
 |
PCDMPy | Phenyl | 3,3-Dimethylpyrrolidine | - | |
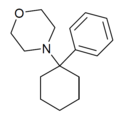 |
PCMo | Phenyl | Morpholine | - | 2201-40-3 |
 |
Methoxy-PCM (2'-MeO-PCMo) | o-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - | 1314323-88-0 |
 |
3'-MeO-PCMo | m-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - | 138873-80-0 |
 |
4'-MeO-PCMo | p-Methoxyphenyl | Morpholine | - | |
 |
Methyl-PCM (4'-Me-PCMo) | p-Tolyl | Morpholine | - | 120803-52-3 |
 |
Hydroxy-methyl-PCM | 2-Methyl-4-hydroxyphenyl | Morpholine | - | 1314323-89-1 |
 |
PYCP | 2-Pyridinyl | Piperidine | - | |
 |
TCM | 2-Thienyl | Methylamino | - | 139401-07-3 |
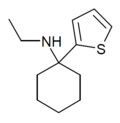 |
TCE | 2-Thienyl | Ethylamino | - | 101589-62-2 |
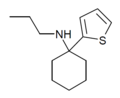 |
TCPr | 2-Thienyl | Propylamino | - | |
 |
Tenocyclidine (TCP) | 2-Thienyl | Piperidine | - | 21500-98-1 |
 |
T3CP | 3-Thienyl | Piperidine | - | 19420-50-9 |
 |
TCPy | 2-Thienyl | Pyrrolidine | - | 22912-13-6 |
 |
Tiletamine | 2-Thienyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | 14176-49-9 |
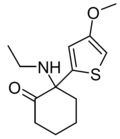 |
MXTE | 4-Methoxy-2-thienyl | Ethylamino | 2-Keto | |
 |
Gacyclidine | 2-Thienyl | Piperidine | 2-Methyl | 68134-81-6 |
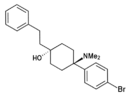 |
BDPC | p-Bromophenyl | Dimethylamino | 4-Phenethyl-4-hydroxy | 77239-98-6 |
 |
C-8813 | p-Bromophenyl | Dimethylamino | 4-(thiophen-2-yl)ethyl-4-hydroxy | 616898-54-5 |
 |
Dimetamine | p-Tolyl | Dimethylamino | 4-Keto | 65619-06-9 |
 |
3''-OH-2'-Me-PCP | o-Tolyl | 3-Hydroxypiperidine | - | |
 |
4''-Ph-4''-OH-PCP | Phenyl | 4-Phenyl-4-hydroxypiperidine | - | 77179-39-6 |
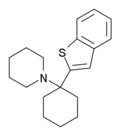 |
BTCP | Benzothiophen-2-yl | Piperidine | - | 112726-66-6 |
 |
BTCPy | Benzothiophen-2-yl | Pyrrolidine | - | |
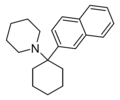 |
GK-189 | Naphthalen-2-yl | Piperidine | - | 81490-58-6 |
Related compounds
Other similar compounds exist where the base ring has been varied, or the amine chain replaced with other groups. More cycloalkane ring sizes have been experimented with than just purely thinking in terms of the cyclohexylamine. The cyclopentyl homologue of PCP is active with around one-tenth the potency, while the cycloheptyl and cyclooctyl derivatives are inactive, though some substituted arylcycloheptylamines retain activity. The requisite cycloalkylketone is reacted with PhMgBr; 3° alcohol is then reacted with NaN3; azide then reduced with LAH. Then in the final step the piperidine ring is constructed with 1-5-dibromo-pentane. Other compounds are known where the cyclohexyl base ring is replaced by rings such as norbornyl, adamantyl, tetralin, oxane, thiane or piperidine.Conformationally constrained analogs have been prepared and researched by Morieti et al.
| Structure | Compound | Aryl Substituent | N Group | Base ring | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
PCPEP | Phenyl | Piperidine | Cyclopentyl | 23036-19-3 |
 |
3F-PCHEPy | 3-Fluorophenyl | Pyrrolidine | Cycloheptyl | |
 |
3-MeO-PBCHP | 3-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane | |
 |
PADP (P2AP) | Phenyl | Piperidine | Adamantyl | 72241-99-7 |
 |
3-MeO-PTP | 3-Methoxyphenyl | Piperidine | Tetralin | |
 |
HHFA | Fused phenyl | Amino | Hexahydrofluorene | |
 |
DHPQ | Phenyl | Decahydroquinoline | ||
 |
POXP | Phenyl | Piperidine | Oxane | |
 |
PTHP | Phenyl | Piperidine | Thiane | |
 |
MPBPip | Phenyl | Piperidine | N-Methylpiperidine | 36882-04-9 |
 |
BnCP | Benzyl | Piperidine | Cyclohexyl | 22912-07-8 |
 |
YNCP | Ethynyl | Piperidine | Cyclohexyl | 51165-02-7 |
 |
ALCP | Allyl | Piperidine | Cyclohexyl | 7418-80-6 |
 |
Piritramide | Replaced by carboxamide | Piperidine | N-(3-cyano-3,3-diphenylpropyl)piperidine | 302-41-0 |
 |
PRE-084 | Phenyl | Morpholinylethylcarboxylate | Cyclohexyl | 138847-85-5 |
 |
Clofenciclan | p-Chlorophenyl | Diethylaminoethoxy | Cyclohexyl | 5632-52-0 |
Further reading
- Morris H, Wallach J (2014). "From PCP to MXE: a comprehensive review of the non-medical use of dissociative drugs". Drug Testing and Analysis. 6 (7–8): 614–32. doi:10.1002/dta.1620. PMID 24678061.
External links
- Synthesis and Effects of PCP Analogs
- Interview with a Ketamine Chemist
- New Drugs: Designing Novel Arylcyclohexylamines
| Inhalational | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Injection |
|
||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
|
Psychedelics (5-HT2A agonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Dissociatives (NMDAR antagonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Deliriants (mAChR antagonists) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adamantanes | |
|---|---|
| Adenosine antagonists | |
| Alkylamines | |
| Ampakines | |
| Arylcyclohexylamines | |
| Benzazepines | |
| Cathinones |
|
| Cholinergics |
|
| Convulsants | |
| Eugeroics | |
| Oxazolines | |
| Phenethylamines |
|
| Phenylmorpholines | |
| Piperazines | |
| Piperidines |
|
| Pyrrolidines | |
| Racetams | |
| Tropanes |
|
| Tryptamines | |
| Others |
|
| AMPAR |
|
|---|---|
| KAR |
|
| NMDAR |
|
|
DAT (DRIs) |
|
||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
NET (NRIs) |
|
||||||||||||||
|
SERT (SRIs) |
|
||||||||||||||
| VMATs | |||||||||||||||
| Others |
|
||||||||||||||

