
Bicaudaviridae
| Bicaudaviridae | |
|---|---|
| |
| Bicaudavirus | |
|
Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | incertae sedis |
| Kingdom: | incertae sedis |
| Phylum: | incertae sedis |
| Class: | incertae sedis |
| Order: | incertae sedis |
| Family: | Bicaudaviridae |
| Genera | |
| |
Bicaudaviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Members of the genus Acidianus serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus (Bicaudavirus) and one species in this family: Acidianus two-tailed virus. However, Sulfolobus tengchongensis spindle-shaped viruses 1 and 2 (STSV1 and STSV2) are regarded to belong to this family also.
Taxonomy
The genus contains one genus, which contains one species:
-
Bicaudavirus
- Acidianus two-tailed virus
Structure
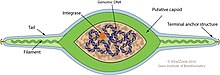
Viruses in Bicaudaviridae are non-enveloped, with lemon-shaped geometries. Genomes are circular dsDNA molecules of around 48–76 kb in length. High-resolution structure was determined by cryo-EM for Sulfolobus monocaudavirus 1 (SMV1) and a lower-resolution structure was determined for Acidianus two-tailed virus (ATV). Virions of both viruses have helical symmetry, with continuous 7-start helices, composed of the single major capsid protein, forming both the tails and the spindle-shaped body. The major capsid protein structure and virion organization of bicaudaviruses are similar to those of archaeal viruses from the families Fuselloviridae, Thaspiviridae, Halspiviridae and Clavaviridae.
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicaudavirus | Lemon-shaped | Helical (C7) | Non-enveloped | Circular | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Viral replication is cytoplasmic. Entry into the host cell is achieved by attachment of the viral proteins to host receptors. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. Diverse species of hyperthermophilic archaea from the order Sulfolobales serve as the natural hosts. Transmission routes are passive diffusion. It has been demonstrated that certain members of the family, namely, STSV2 and Sulfolobus monocaudavirus 1 (SMV1), induce cell gigantism by blocking the expression of the cell division genes and arresting the cell cycle in the S phase. The diameter of infected cells increases up to 20 times, resulting in 8,000-fold increase in volume compared to noninfected cells.
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bicaudavirus | Archea: acidianus | None | Injection | Budding | Cytoplasm | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
History
This family was first described by the team led by D. Prangishvili in 2005.
The name is derived from the Latin word 'bi' and 'cauda' meaning 'two-tail'.

