Mdm2
Mouse double minute 2 homolog (MDM2) also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MDM2 gene. Mdm2 is an important negative regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor. Mdm2 protein functions both as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that recognizes the N-terminal trans-activation domain (TAD) of the p53 tumor suppressor and as an inhibitor of p53 transcriptional activation.
Discovery and expression in tumor cells
The murine double minute (mdm2) oncogene, which codes for the Mdm2 protein, was originally cloned, along with two other genes (mdm1 and mdm3) from the transformed mouse cell line 3T3-DM. Mdm2 overexpression, in cooperation with oncogenic Ras, promotes transformation of primary rodent fibroblasts, and mdm2 expression led to tumor formation in nude mice. The human homologue of this protein was later identified and is sometimes called Hdm2. Further supporting the role of mdm2 as an oncogene, several human tumor types have been shown to have increased levels of Mdm2, including soft tissue sarcomas and osteosarcomas as well as breast tumors. The MDM2 oncoprotein ubiquitinates and antagonizes p53 but may also carry out p53-independent functions. MDM2 supports the Polycomb-mediated repression of lineage-specific genes, independent of p53. MDM2 depletion in the absence of p53 promoted the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and diminished clonogenic survival of cancer cells. Most of the MDM2-controlled genes also responded to the inactivation of the Polycomb Repressor Complex 2 (PRC2) and its catalytic component EZH2. MDM2 physically associated with EZH2 on chromatin, enhancing the trimethylation of histone 3 at lysine 27 (H3K27me3) and the ubiquitination of histone 2A at lysine 119 (H2AK119) at its target genes. Removing MDM2 simultaneously with the H2AK119 E3 ligase Ring1B/RNF2 further induced these genes and synthetically arrested cell proliferation.
An additional Mdm2 family member, Mdm4 (also called MdmX), has been discovered and is also an important negative regulator of p53.
MDM2 is also required for organ development and tissue homeostasis because unopposed p53 activation leads to p53-overactivation-dependent cell death, referred to as podoptosis. Podoptosis is caspase-independent and, therefore, different from apoptosis. The mitogenic role of MDM2 is also needed for wound healing upon tissue injury, while MDM2 inhibition impairs re-epithelialization upon epithelial damage. In addition, MDM2 has p53-independent transcription factor-like effects in nuclear factor-kappa beta (NFκB) activation. Therefore, MDM2 promotes tissue inflammation and MDM2 inhibition has potent anti-inflammatory effects in tissue injury. So, MDM2 blockade had mostly anti-inflammatory and anti-mitotic effects that can be of additive therapeutic efficacy in inflammatory and hyperproliferative disorders such as certain cancers or lymphoproliferative autoimmunity, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or crescentic glomerulonephritis.
Ubiquitination target: p53
The key target of Mdm2 is the p53 tumor suppressor. Mdm2 has been identified as a p53 interacting protein that represses p53 transcriptional activity. Mdm2 achieves this repression by binding to and blocking the N-terminal trans-activation domain of p53. Mdm2 is a p53 responsive gene—that is, its transcription can be activated by p53. Thus when p53 is stabilized, the transcription of Mdm2 is also induced, resulting in higher Mdm2 protein levels.
E3 ligase activity
The E3 ubiquitin ligase MDM2 is a negative regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. MDM2 binds and ubiquitinates p53, facilitating it for degradation. p53 can induce transcription of MDM2, generating a negative feedback loop. Mdm2 also acts as an E3 ubiquitin ligase, targeting both itself and p53 for degradation by the proteasome (see also ubiquitin). Several lysine residues in p53 C-terminus have been identified as the sites of ubiquitination, and it has been shown that p53 protein levels are downregulated by Mdm2 in a proteasome-dependent manner. Mdm2 is capable of auto-polyubiquitination, and in complex with p300, a cooperating E3 ubiquitin ligase, is capable of polyubiquitinating p53. In this manner, Mdm2 and p53 are the members of a negative feedback control loop that keeps the level of p53 low in the absence of p53-stabilizing signals. This loop can be interfered with by kinases and genes like p14arf when p53 activation signals, including DNA damage, are high.
Structure and function
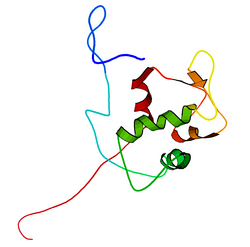
The full-length transcript of the mdm2 gene encodes a protein of 491 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 56kDa. This protein contains several conserved structural domains including an N-terminal p53 interaction domain, the structure of which has been solved using x-ray crystallography. The Mdm2 protein also contains a central acidic domain (residues 230-300). The phosphorylation of residues within this domain appears to be important for regulation of Mdm2 function. In addition, this region contains nuclear export and import signals that are essential for proper nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of Mdm2. Another conserved domain within the Mdm2 protein is a zinc finger domain, the function of which is poorly understood.
Mdm2 also contains a C-terminal RING domain (amino acid residues 430-480), which contains a Cis3-His2-Cis3 consensus that coordinates two ions of zinc. These residues are required for zinc binding, which is essential for proper folding of the RING domain. The RING domain of Mdm2 confers E3 ubiquitin ligase activity and is sufficient for E3 ligase activity in Mdm2 RING autoubiquitination. The RING domain of Mdm2 is unique in that it incorporates a conserved Walker A or P-loop motif characteristic of nucleotide binding proteins, as well as a nucleolar localization sequence. The RING domain also binds specifically to RNA, although the function of this is poorly understood.
Regulation
There are several known mechanisms for regulation of Mdm2. One of these mechanisms is phosphorylation of the Mdm2 protein. Mdm2 is phosphorylated at multiple sites in cells. Following DNA damage, phosphorylation of Mdm2 leads to changes in protein function and stabilization of p53. Additionally, phosphorylation at certain residues within the central acidic domain of Mdm2 may stimulate its ability to target p53 for degradation. HIPK2 is a protein that regulates Mdm2 in this way. The induction of the p14arf protein, the alternate reading frame product of the p16INK4a locus, is also a mechanism of negatively regulating the p53-Mdm2 interaction. p14arf directly interacts with Mdm2 and leads to up-regulation of p53 transcriptional response. ARF sequesters Mdm2 in the nucleolus, resulting in inhibition of nuclear export and activation of p53, since nuclear export is essential for proper p53 degradation.
Inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 interaction include the cis-imidazoline analog nutlin.
Levels and stability of Mdm2 are also modulated by ubiquitylation. Mdm2 auto ubiquitylates itself, which allows for its degradation by the proteasome. Mdm2 also interacts with a ubiquitin specific protease, USP7, which can reverse Mdm2-ubiquitylation and prevent it from being degraded by the proteasome. USP7 also protects from degradation the p53 protein, which is a major target of Mdm2. Thus Mdm2 and USP7 form an intricate circuit to finely regulate the stability and activity of p53, whose levels are critical for its function.
Interactions

Mdm2 has been shown to interact with:
Mdm2 p53-independent role
Mdm2 overexpression was shown to inhibit DNA double-strand break repair mediated through a novel, direct interaction between Mdm2 and Nbs1 and independent of p53. Regardless of p53 status, increased levels of Mdm2, but not Mdm2 lacking its Nbs1-binding domain, caused delays in DNA break repair, chromosomal abnormalities, and genome instability. These data demonstrated Mdm2-induced genome instability can be mediated through Mdm2:Nbs1 interactions and independent from its association with p53.
Further reading
- Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, George DL (May 1987). "Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 13 (3): 235–44. doi:10.1007/BF01535205. PMID 3474784. S2CID 27300300.
- Chen J, Lin J, Levine AJ (January 1995). "Regulation of transcription functions of the p53 tumor suppressor by the mdm-2 oncogene". Molecular Medicine. 1 (2): 142–52. doi:10.1007/BF03401562. PMC 2229942. PMID 8529093.
- Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH, Weissman AM (March 2000). "Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein ligase for itself and p53". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (12): 8945–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.12.8945. PMID 10722742. S2CID 25630836.
- Freedman DA, Wu L, Levine AJ (January 1999). "Functions of the MDM2 oncoprotein". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 55 (1): 96–107. doi:10.1007/s000180050273. PMID 10065155. S2CID 20034406.
- Hay TJ, Meek DW (July 2000). "Multiple sites of in vivo phosphorylation in the MDM2 oncoprotein cluster within two important functional domains". FEBS Letters. 478 (1–2): 183–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01850-0. PMID 10922493. S2CID 40688636.
- Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (December 1997). "Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53". FEBS Letters. 420 (1): 25–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01480-4. PMID 9450543. S2CID 29014813.
- Honda R, Yasuda H (March 2000). "Activity of MDM2, a ubiquitin ligase, toward p53 or itself is dependent on the RING finger domain of the ligase". Oncogene. 19 (11): 1473–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203464. PMID 10723139. S2CID 8734229.
- Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH (May 1997). "Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2". Nature. 387 (6630): 299–303. Bibcode:1997Natur.387..299K. doi:10.1038/387299a0. PMID 9153396. S2CID 4329670.
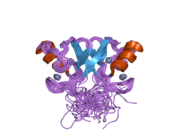
- Kussie PH, Gorina S, Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Moreau J, Levine AJ, Pavletich NP (November 1996). "Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain". Science. 274 (5289): 948–53. Bibcode:1996Sci...274..948K. doi:10.1126/science.274.5289.948. PMID 8875929. S2CID 33081920.
- Meek DW, Knippschild U (December 2003). "Posttranslational modification of MDM2". Molecular Cancer Research. 1 (14): 1017–26. PMID 14707285.
- Midgley CA, Desterro JM, Saville MK, Howard S, Sparks A, Hay RT, Lane DP (May 2000). "An N-terminal p14ARF peptide blocks Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination in vitro and can activate p53 in vivo". Oncogene. 19 (19): 2312–23. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203593. PMID 10822382. S2CID 24814361.
- Momand J, Wu HH, Dasgupta G (January 2000). "MDM2--master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein". Gene. 242 (1–2): 15–29. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00487-4. PMID 10721693.
- Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (June 1992). "The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation". Cell. 69 (7): 1237–45. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-R. PMID 1535557. S2CID 22594319.
- Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y, Prives C (October 1997). "DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2". Cell. 91 (3): 325–34. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80416-X. PMID 9363941. S2CID 11328296.
- Tao W, Levine AJ (June 1999). "P19(ARF) stabilizes p53 by blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Mdm2". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (12): 6937–41. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.6937T. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.12.6937. PMC 22020. PMID 10359817.
- Tao W, Levine AJ (March 1999). "Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of oncoprotein Hdm2 is required for Hdm2-mediated degradation of p53". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (6): 3077–80. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.3077T. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3077. PMC 15897. PMID 10077639.
External links
|
PDB gallery
| |
|---|---|
| Ligand |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Intracellular signaling P+Ps |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nucleus |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mitochondrion |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other/ungrouped | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6.1: Carbon-Oxygen | |
|---|---|
| 6.2: Carbon-Sulfur | |
| 6.3: Carbon-Nitrogen | |
| Biotin dependent carboxylation | |
|---|---|
| Other | |
|
Chaperones/ protein folding |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein targeting | |||||
|
Ubiquitin (ubiquitylation) |
|||||
|
Ubiquitin-like proteins (UBL) |
|
||||