Potyvirus
| Potyvirus | |
|---|---|

| |
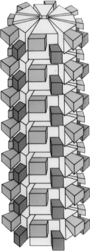
| Plum pox virus genome with electron micrograph and model of virions | |
|
Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Stelpaviricetes |
| Order: | Patatavirales |
| Family: | Potyviridae |
| Genus: | Potyvirus |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Potyvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Potyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. The genus is named after member virus potato virus Y. Potyviruses account for about thirty percent of the currently known plant viruses. Like begomoviruses, members of this genus may cause significant losses in agricultural, pastoral, horticultural, and ornamental crops. More than 200 species of aphids spread potyviruses, and most are from the subfamily Aphidinae (genera Macrosiphum and Myzus). The genus contains 190 species.
Virology
Structure
The virion is non-enveloped with a flexuous and filamentous nucleocapsid, 680 to 900 nanometers (nm) long and is 11–20 nm in diameter. The nucleocapsid contains around 2000 copies of the capsid protein. The symmetry of the nucleocapsid is helical with a pitch of 3.4 nm.
Genome
The genome is a linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA ranging in size from 9,000–12,000 nucleotide bases. Most potyviruses have non-segmented genomes, though a number of species are bipartite. The base composition is: 21–23.51–26% G; 23–30.15–44% A; 14.9–22.41–28% C; 15.6–24.41–30.9% U.
In the species with a single genome, at the 5' end a protein is covalently linked (the VPg protein). It encodes a single open reading frame (ORF) expressed as a 350 kDa polyprotein precursor. This is processed into ten smaller proteins: protein 1 protease (P1-Pro), helper component protease (HC-Pro), protein 3 (P3), cylindrical inclusion (CI), viral protein genome-linked (Vpg), nuclear inclusion A (NIa), nuclear inclusion B (NIb), capsid protein (CP) and two small putative proteins known as 6K1 and 6K2. The P3 cistron also encodes a second protein—P3N-PIPO—which is generated by a +2 frameshift.
Proteins
Properties of the viral protein:
P1-Pro (~33 kiloDaltons (kDa) in molecular weight) is a serine protease.
HC-Pro (~52 KDa) is a protease that is also involved in aphid transmission. As a protease it cleaves a glycine-glycine dipeptide at its own C-terminus. It also interacts with eukaryotic initiation factor 4 (eIF4). It acts as a viral RNA silencing suppressor.
P3 (~41 kDa) the function is not known. It interacts with large subunit of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase.
CI (~71 kDa) is an RNA helicase with ATPase activity. It is also involved in membrane attachment.
NIa (~50 kDa) is cleaved into NIa-Pro a protease (~27 kDa) and the VPg (~22 kDa) protein.
NIb (~59 kDa) is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.
6K1 (~6 kDa) the function is not known. 6K2 (~6 kDa) protein, having a single trans membrane domain, is accumulating in the host cellular membranes and is thought to play a role in forming the replication vesicles of the virus.
P3N-PIPO (~25 kDa) the function is not known but it appears to be essential. It interacts with both the large and small subunits of the ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase.
CP the capsid protein ranges between 30 and 35 kDa in weight.
Pretty interesting sweet potato potyviral ORF (PISPO), Alkylation B (AlkB), and inosine triphosphate pyrophosphatase (known as ITPase or HAM1) are protein domains identified in atypical potyviruses.
VPg protein interacts with eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E). This interaction appears to be essential to viral infectivity. Two proteases, P1 and the helper component protease (HC) catalyse only autoproteolytic reactions at their respective C termini. The remaining cleavage reactions are catalysed by either trans-proteolytic or autoproteolytic mechanisms by the small nuclear inclusion protein (NIa-Pro). This latter protein is an evolutionary homology of the picornavirus 3C proteinase.
Life cycle

Replication may occur in the cytoplasm,nuclei, chloroplasts, Golgi apparatus, cell vacuoles or more rarely in unusual sites.
Potyviruses make proteinaceous inclusions in infected plant cells. These may be crystals in either the cytoplasm or in the nucleus, as amorphous X-bodies, membranous bodies, viroplasms or pinwheels. The inclusions may or may not (depending on the species) contain virions. These inclusions can be seen in the light microscope in leaf strips of infected plant tissue stained with Orange-Green (protein stain) but not Azure A (nucleic acid stain). There are four different kinds of potyvirus inclusions.
Replication follows the positive-stranded RNA virus replication model. Positive-stranded RNA virus transcription is the method of transcription. Translation takes place by -1 ribosomal frameshifting. The virus exits the host cell by tubule-guided viral movement. Plants serve as the natural host. The virus is transmitted via a vector (insects). Transmission routes are vector and mechanical.
Evolution
Potyviruses evolved between 6,600 and 7,250 years ago. They appear to have evolved in southwest Eurasia or north Africa. The estimated mutation rate is about 1.15×10−4 nucleotide substitutions/site/year.
Geographical spread
Agriculture was introduced into Australia in the 18th century. This introduction also included plant pathogens. Thirty eight potyvirus species have been isolated in Australia. Eighteen potyviruses have been found only in Australia and are presumed to be endemic there. The remaining twenty appear to have been introduced with agriculture.
Taxonomy
Potyvirus contains the following species:
- African eggplant mosaic virus
- Algerian watermelon mosaic virus
- Alstroemeria mosaic virus
- Alternanthera mild mosaic virus
- Amaranthus leaf mottle virus
- Amazon lily mosaic virus
- Angelica virus Y
- Apium virus Y
- Araujia mosaic virus
- Arracacha mottle virus
- Asparagus virus 1
- Banana bract mosaic virus
- Barbacena virus Y
- Basella rugose mosaic virus
- Bean common mosaic necrosis virus
- Bean common mosaic virus
- Bean yellow mosaic virus
- Beet mosaic virus
- Begonia flower breaking virus
- Bidens mosaic virus
- Bidens mottle virus
- Blue squill virus A
- Brugmansia mosaic virus
- Brugmansia suaveolens mottle virus
- Butterfly flower mosaic virus
- Calanthe mild mosaic virus
- Calla lily latent virus
- Callistephus mottle virus
- Canna yellow streak virus
- Carnation vein mottle virus
- Carrot thin leaf virus
- Carrot virus Y
- Catharanthus mosaic virus
- Celery mosaic virus
- Ceratobium mosaic virus
- Chilli ringspot virus
- Chilli veinal mottle virus
- Chinese artichoke mosaic virus
- Clitoria virus Y
- Clover yellow vein virus
- Cocksfoot streak virus
- Colombian datura virus
- Commelina mosaic virus
- Costus stripe mosaic virus
- Cowpea aphid-borne mosaic virus
- Cucurbit vein banding virus
- Cypripedium virus Y
- Cyrtanthus elatus virus A
- Daphne mosaic virus
- Daphne virus Y
- Dasheen mosaic virus
- Datura shoestring virus
- Dendrobium chlorotic mosaic virus
- Dioscorea mosaic virus
- Diuris virus Y
- Donkey orchid virus A
- East Asian Passiflora distortion virus
- East Asian Passiflora virus
- Endive necrotic mosaic virus
- Euphorbia ringspot virus
- Freesia mosaic virus
- Fritillary virus Y
- Gloriosa stripe mosaic virus
- Gomphocarpus mosaic virus
- Habenaria mosaic virus
- Hardenbergia mosaic virus
- Henbane mosaic virus
- Hibbertia virus Y
- Hippeastrum mosaic virus
- Hyacinth mosaic virus
- Impatiens flower break virus
- Iris fulva mosaic virus
- Iris mild mosaic virus
- Iris severe mosaic virus
- Japanese yam mosaic virus
- Jasmine virus T
- Johnsongrass mosaic virus
- Kalanchoe mosaic virus
- Keunjorong mosaic virus
- Konjac mosaic virus
- Leek yellow stripe virus
- Lettuce Italian necrotic virus
- Lettuce mosaic virus
- Lily mottle virus
- Lily virus Y
- Lupinus mosaic virus
- Lycoris mild mottle virus
- Maize dwarf mosaic virus
- Malva vein clearing virus
- Mashua virus Y
- Meadow saffron breaking virus
- Mediterranean ruda virus
- Moroccan watermelon mosaic virus
- Narcissus degeneration virus
- Narcissus late season yellows virus
- Narcissus yellow stripe virus
- Nerine yellow stripe virus
- Noni mosaic virus
- Nothoscordum mosaic virus
- Onion yellow dwarf virus
- Ornithogalum mosaic virus
- Ornithogalum virus 2
- Ornithogalum virus 3
- Panax virus Y
- Papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus
- Papaya ringspot virus
- Paris mosaic necrosis virus
- Paris virus 1
- Parsnip mosaic virus
- Passiflora chlorosis virus
- Passiflora mottle virus
- Passion fruit woodiness virus
- Pea seed-borne mosaic virus
- Peanut mottle virus
- Pecan mosaic-associated virus
- Pennisetum mosaic virus
- Pepper mottle virus
- Pepper severe mosaic virus
- Pepper veinal mottle virus
- Pepper yellow mosaic virus
- Peru tomato mosaic virus
- Pfaffia mosaic virus
- Platycodon mild mottle virus
- Pleione flower breaking virus
- Pleione virus Y
- Plum pox virus
- Pokeweed mosaic virus
- Potato virus A
- Potato virus V
- Potato virus Y
- Potato yellow blotch virus
- Ranunculus leaf distortion virus
- Ranunculus mild mosaic virus
- Ranunculus mosaic virus
- Rhopalanthe virus Y
- Saffron latent virus
- Sarcochilus virus Y
- Scallion mosaic virus
- Shallot yellow stripe virus
- Sorghum mosaic virus
- Soybean mosaic virus
- Spiranthes mosaic virus 3
- Sudan watermelon mosaic virus
- Sugarcane mosaic virus
- Sunflower chlorotic mottle virus
- Sunflower mild mosaic virus
- Sunflower mosaic virus
- Sunflower ring blotch virus
- Sweet potato feathery mottle virus
- Sweet potato latent virus
- Sweet potato mild speckling virus
- Sweet potato virus 2
- Sweet potato virus C
- Sweet potato virus G
- Tamarillo leaf malformation virus
- Telfairia mosaic virus
- Telosma mosaic virus
- Thunberg fritillary mosaic virus
- Tobacco etch virus
- Tobacco mosqueado virus
- Tobacco vein banding mosaic virus
- Tobacco vein mottling virus
- Tomato necrotic stunt virus
- Tradescantia mild mosaic virus
- Tuberose mild mosaic virus
- Tuberose mild mottle virus
- Tulip breaking virus
- Tulip mosaic virus
- Turnip mosaic virus
- Twisted-stalk chlorotic streak virus
- Ugandan passiflora virus
- Vallota mosaic virus
- Vanilla distortion mosaic virus
- Verbena virus Y
- Watermelon leaf mottle virus
- Watermelon mosaic virus
- Wild melon banding virus
- Wild onion symptomless virus
- Wild potato mosaic virus
- Wild tomato mosaic virus
- Wisteria vein mosaic virus
- Yam mild mosaic virus
- Yam mosaic virus
- Yambean mosaic virus
- Zantedeschia mild mosaic virus
- Zea mosaic virus
- Zucchini shoestring virus
- Zucchini tigre mosaic virus
- Zucchini yellow fleck virus
- Zucchini yellow mosaic virus
A further four viruses were previously classified as species in this genus but were abolished due to lack of genetic sequence information:
- Cowpea green vein banding virus
- Groundnut eyespot virus
- Helenium virus Y
- Tropaeolum mosaic virus
Species groups
Potyviruses were further divided into the PVY, SCMV, BYMV, BCMV species groups in 1992. Gibbs and Ohshima 2010 produced a more extensive molecular phylogeny with the same four, but also several new groups: the BtMV, ChVMV, DaMV, OYDV, PRSV, TEV, and TuMV.
PVY
Contains 16 species including the type species of the genus (potato virus Y). The primary hosts are: Nine Solanaceae, three Amaranthus, three Asteraceae, one Lilium, and one Amaryllis.
Bibliography
- Ward, CW; Shukla, DD (1991). "Taxonomy of potyviruses: current problems and some solutions". Intervirology. 32 (5): 269–96. doi:10.1159/000150211. PMID 1657820.
- King, Andrew M. Q.; et al., eds. (2012). "Potyvirus". Virus taxonomy : classification and nomenclature of viruses : ninth report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. London: Academic Press. pp. 926–1072. ISBN 978-0123846846. Retrieved 9 December 2014.