
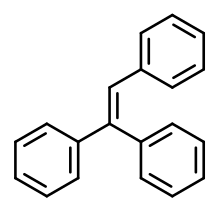
Triphenylethylene
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.359 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H16 |
| Molar mass | 256.348 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Triphenylethylene (TPE) is a simple aromatic hydrocarbon that possesses weak estrogenic activity. Its estrogenic effects were discovered in 1937. TPE was derived from structural modification of the more potent estrogen diethylstilbestrol, which is a member of the stilbestrol group of nonsteroidal estrogens.
TPE is the parent compound of a group of nonsteroidal estrogen receptor ligands. It includes the estrogens chlorotrianisene, desmethylchlorotrianisene, estrobin (DBE), M2613, triphenylbromoethylene, triphenylchloroethylene, triphenyliodoethylene, triphenylmethylethylene; the selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) afimoxifene, brilanestrant, broparestrol, clomifene, clomifenoxide, droloxifene, endoxifen, etacstil, fispemifene, idoxifene, miproxifene, miproxifene phosphate, nafoxidine, ospemifene, panomifene, and toremifene. The antiestrogen ethamoxytriphetol (MER-25) is also closely related, but is technically not a derivative of TPE and is instead a triphenylethanol derivative. The tamoxifen metabolite and aromatase inhibitor norendoxifen is also a TPE derivative. In addition to their estrogenic activity, various TPE derivatives like tamoxifen and clomifene have been found to act as protein kinase C inhibitors.
The affinity of triphenylethylene for the rat estrogen receptor is about 0.002% relative to estradiol. For comparison, the relative binding affinities of derivatives of triphenylethylene were 1.6% for tamoxifen, 175% for afimoxifene (4-hydroxytamoxifen), 15% for droloxifene, 1.4% for toremifene (4-chlorotamoxifen), 0.72% for clomifene, and 0.72% for nafoxidine.
See also
- List of SERMs
- Benzothiophene – parent compound for another group of nonsteroidal SERMs that includes raloxifene
- Phenanthrene – parent compound of steroidal estrogens like estradiol
- Chrysene – parent compound of a group of nonsteroidal weak estrogens that includes 2,8-DHHHC and tetrahydrochrysene
- Doisynolic acid – parent compound of a group of nonsteroidal estrogens that includes doisynoestrol
- Allenolic acid – parent compound of a group of nonsteroidal estrogens that includes methallenestril