
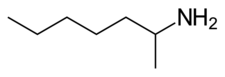
Tuaminoheptane
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Heptin, Heptadrine, Tuamine |
| Other names | Tuamine; 2-Aminoheptane; 2-Heptanamine; 1-Methylhexylamine |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.233 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H17N |
| Molar mass | 115.220 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 0.766 g/mL g/cm3 |
| |
| |
Tuaminoheptane (INN, BAN; brand names Heptin, Heptadrine, Tuamine; also known as tuamine and 2-aminoheptane) is a sympathomimetic agent and vasoconstrictor which was formerly used as a nasal decongestant. It has also been used as a stimulant.
Tuaminoheptane has been found to act as a reuptake inhibitor and releasing agent of norepinephrine, which may underlie its decongestant and stimulant effects. It is an alkylamine. The chemical structure of the drug differs from that of other norepinephrine releasing agents, such as the phenethylamines, which, in contrast to tuaminoheptane, have an aromatic ring in their structure. Tuaminoheptane is also a skin irritant and can cause contact dermatitis via inhibition of volume-regulated anion channels, which limits its usefulness as a decongestant.
Tuaminoheptane is on the 2011 list of prohibited substances published by the World Anti-Doping Agency.
See also
External links
- The World Anti-Doping Code. The 2011 Prohibited List. International Standard Archived 2012-05-13 at the Wayback Machine
|
Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01)
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical |
|
||||||||||
| Systemic use: Sympathomimetics |
|||||||||||
| |||||||||||