Dextromethorphan
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation |
/ˌdɛk.stroʊ.məˈθɔːrˌfæn/ DEK-stroh-məth-OR-fan |
| Trade names | Robitussin, Delsym, others |
| Other names | DXM |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682492 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
By mouth |
| Drug class | Antitussive,hallucinogen (dissociative) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 11% |
| Metabolism | Liver enzymes: major CYP2D6, minor CYP3A4, and minor CYP3A5 |
| Elimination half-life | 2–4 hours (extensive metabolizers); 24 hours (poor metabolizers) |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.321 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H25NO |
| Molar mass | 271.404 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 111 °C (232 °F) |
| |
| |
|
| |
Dextromethorphan (DXM) is a cough suppressant in over-the-counter cold and cough medicines. It affects NMDA, glutamate-1, and sigma-1 receptors in the brain, all of which have been implicated in the pathophysiology of depression. In 2022, the FDA approved a formulation of it combined with bupropion named Auvelity to serve as a rapid acting antidepressant in patients with major depressive disorder. It is sold in syrup, instant release tablet, extended release tablet, spray, and lozenge forms.
It is in the morphinan class of medications with sedative, dissociative, and stimulant properties (at lower doses). Dextromethorphan does not have a significant affinity for the mu-opioid receptor activity typical of morphinan compounds and exerts its therapeutic effects through several other receptors. In its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as a white powder.
Dextromethorphan is also used recreationally. When exceeding approved dosages, dextromethorphan acts as a dissociative hallucinogen. It has multiple mechanisms of action, including actions as a nonselective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and a sigma-1 receptor agonist. Dextromethorphan and its major metabolite, dextrorphan, also block the NMDA receptor at high doses, which produces effects similar to other dissociative anesthetics such as ketamine, nitrous oxide, and phencyclidine.
It was patented in 1949 and approved for medical use in 1953.
Medical uses
Cough suppression
The primary use of dextromethorphan is as a cough suppressant, for the temporary relief of cough caused by minor throat and bronchial irritation (such as commonly accompanies the flu and common cold), or from inhaled particle irritants, as well as chronic cough at a higher dosage.
Pseudobulbar affect
In 2010, the FDA approved the combination drug dextromethorphan/quinidine, brand name Neudexta for the treatment of pseudobulbar affect (uncontrollable laughing/crying). Dextromethorphan is the actual therapeutic agent in the combination; quinidine merely serves to inhibit the enzymatic degradation of dextromethorphan and thereby increase its circulating concentrations via inhibition of CYP2D6.
Major depressive disorder
The combination medicine dextromethorphan/bupropion is approved for major depressive disorder due to its action on the NMDA receptor.
Available forms
Dextromethorphan is available alone in the form of cough syrup and pills as well as in combination with other agents. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is available as dextromethorphan/quinidine (Nuedexta) for the treatment of pseudobulbar affect and as dextromethorphan/bupropion (Auvelity) for treatment-resistant major depressive disorder.
Contraindications
Because dextromethorphan can trigger a histamine release (allergic reaction), atopic children, who are especially susceptible to allergic reactions, should be administered dextromethorphan only if absolutely necessary, and only under the strict supervision of a healthcare professional.
Adverse effects
Side effects of dextromethorphan at normal therapeutic doses can include:
A rare side effect is respiratory depression.
Neurotoxicity
Dextromethorphan was once thought to cause Olney's lesions when administered intravenously; however, this was later proven inconclusive, due to lack of research on humans. Tests were performed on rats, giving them 50 mg or more every day for as long as a month. Neurotoxic changes, including vacuolation, have been observed in posterior cingulate and retrosplenial cortices of rats administered other NMDA receptor antagonists such as PCP, but not with dextromethorphan.
Dependence and withdrawal
In many documented cases, dextromethorphan has produced psychological dependence in people who used it recreationally. It is considered less addictive than other common cough suppressants, such as the weak opiate codeine. Since dextromethorphan also acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, users report that regular recreational use over a long period of time can cause withdrawal symptoms similar to those of antidepressant discontinuation syndrome. Additionally, disturbances have been reported in sleep, senses, movement, mood, and thinking.
Overdose
Adverse effects of dextromethorphan in overdose at doses 3 to 10 times the recommended therapeutic dose:
- mild nausea
- restlessness
- insomnia
- talking fast
- dilated pupils
- glassy eyes
- dizziness
At doses 11 to 75 times the recommended therapeutic dose:
- hallucinations
- dissociation
- vomiting
- blurred vision
- double vision
- bloodshot eyes
- dilated pupils
- sweating
- fever
- bruxia (teeth grinding)
- hypotension
- hypertension
- tachycardia
- shallow respiration
- diarrhea
- urinary retention
- muscle spasms
- sedation
- paresthesia
- blackouts
- inability to focus eyes
- skin rash
- severe itchiness
- acute psychosis
Episodic acute psychosis can occur when high doses of dextromethorphan are taken for recreational use, and an abundance of psychiatric symptoms can result, including dissociation and other PCP-like symptoms.
Interactions
Serotonin syndrome may result from the combined use of dextromethorphan and serotonergic antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRIs) or monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOIs). Further research is needed to determine whether doses of dextromethorphan beyond those normally used therapeutically are needed to produce this effect. In any case, dextromethorphan should not be taken with MAOIs due to the possibility of this complication. Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition that can occur rapidly, due to a buildup of an excessive amount of serotonin in the body.
Patients who are taking dextromethorphan should exercise caution when drinking grapefruit juice or eating grapefruit, as compounds in grapefruit affect a number of drugs, including dextromethorphan, through the inhibition of the cytochrome P450 system in the liver, and can lead to excessive accumulation of the drug which both increases and prolongs effects. Grapefruit and grapefruit juices (especially white grapefruit juice, but also including other citrus fruits such as bergamot and lime, as well as a number of noncitrus fruits) generally are recommended to be avoided while using dextromethorphan and numerous other medications.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
| Site | DXM | DXO | Species | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMDAR (MK-801) |
2,120–8,945 | 486–906 | Rat | |
| σ1 | 142–652 | 118–481 | Rat | |
| σ2 | 11,060–22,864 | 11,325–15,582 | Rat | |
| MOR | 1,280 ND |
420 >1,000 |
Rat Human |
|
| DOR | 11,500 | 34,700 | Rat | |
| KOR | 7,000 | 5,950 | Rat | |
| SERT | 23–40 | 401–484 | Rat | |
| NET | ≥240 | ≥340 | Rat | |
| DAT | >1,000 | >1,000 | Rat | |
| 5-HT1A | >1,000 | >1,000 | Rat | |
| 5-HT1B/1D | 61% at 1 μM | 54% at 1 μM | Rat | |
| 5-HT2A | >1,000 | >1,000 | Rat | |
| α1 | >1,000 | >1,000 | Rat | |
| α2 | 60% at 1 μM | >1,000 | Rat | |
| β | >1,000 | 35% at 1 μM | Rat | |
| D2 | >1,000 | >1,000 | Rat | |
| H1 | >1,000 | 95% at 1 μM | Rat | |
| mAChRs | >1,000 | 100% at 1 μM | Rat | |
| nAChRs | 700–8,900 (IC50) |
1,300–29,600 (IC50) |
Rat | |
| VDSCs | >50,000 (IC50) | ND | Rat | |
| Values are Ki (nM), unless otherwise noted. The smaller the value, the more strongly the drug binds to the site. | ||||
Dextromethorphan has been found to possess the following actions (<1 μM) using rat tissues:
- Uncompetitive antagonist of the NMDA receptor via the MK-801/PCP site
- SERT and NET blocker (cf. serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor)
- Sigma σ1 receptor agonist
- Negative allosteric modulator of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- Ligand of the serotonin 5-HT1B/1D, histamine H1, α2-adrenergic, and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Dextromethorphan is a prodrug of dextrorphan, which is the actual mediator of most of its dissociative effects through acting as a more potent NMDA receptor antagonist than dextromethorphan itself. What role, if any, (+)-3-methoxymorphinan, dextromethorphan's other major metabolite, plays in its effects is not entirely clear.
Pharmacokinetics
Following oral administration, dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, where it enters the bloodstream and crosses the blood–brain barrier.
At therapeutic doses, dextromethorphan acts centrally (meaning that it acts on the brain) as opposed to locally (on the respiratory tract). It elevates the threshold for coughing, without inhibiting ciliary activity. Dextromethorphan is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and converted into the active metabolite dextrorphan in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme CYP2D6. The average dose necessary for effective antitussive therapy is between 10 and 45 mg, depending on the individual. The International Society for the Study of Cough recommends "an adequate first dose of medication is 60 mg in the adult and repeat dosing should be infrequent rather than qds recommended."
Dextromethorphan has an elimination half-life of approximately 4 hours in individuals with an extensive metabolizer phenotype; this is increased to approximately 13 hours when dextromethorphan is given in combination with quinidine. The duration of action after oral administration is about three to eight hours for dextromethorphan hydrobromide, and 10 to 12 hours for dextromethorphan polistirex. Around one in 10 of the Caucasian population has little or no CYP2D6 enzyme activity, leading to long-lived high drug levels.
Metabolism
The first pass through the hepatic portal vein results in some of the drug being metabolized by O-demethylation into an active metabolite of dextromethorphan called dextrorphan, the 3-hydroxy derivative of dextromethorphan. The therapeutic activity of dextromethorphan is believed to be caused by both the drug and this metabolite. Dextromethorphan also undergoes N-demethylation (to 3-methoxymorphinan or MEM), and partial conjugation with glucuronic acid and sulfate ions. Hours after dextromethorphan therapy, (in humans) the metabolites (+)-3-hydroxy-N-methylmorphinan, (+)-3-morphinan, and traces of the unchanged drug are detectable in the urine.
A major metabolic catalyst involved is the cytochrome P450 enzyme known as 2D6, or CYP2D6. A significant portion of the population has a functional deficiency in this enzyme and are known as poor CYP2D6 metabolizers. O-demethylation of dextromethorphan to dextrorphan contributes to at least 80% of the dextrorphan formed during dextromethorphan metabolism. As CYP2D6 is a major metabolic pathway in the inactivation of dextromethorphan, the duration of action and effects of dextromethorphan can be increased by as much as three times in such poor metabolizers. In one study on 252 Americans, 84.3% were found to be "fast" (extensive) metabolizers, 6.8% to be "intermediate" metabolizers, and 8.8% were "slow" metabolizers of dextromethorphan. A number of alleles for CYP2D6 are known, including several completely inactive variants. The distribution of alleles is uneven amongst ethnic groups.
A large number of medications are potent inhibitors of CYP2D6. Some types of medications known to inhibit CYP2D6 include certain SSRIs and tricyclic antidepressants, some antipsychotics, and the commonly available antihistamine diphenhydramine. Therefore, the potential of interactions exists between dextromethorphan and medications that inhibit this enzyme, particularly in slow metabolizers.
Dextromethorphan is also metabolized by CYP3A4. N-demethylation is primarily accomplished by CYP3A4, contributing to at least 90% of the MEM formed as a primary metabolite of dextromethorphan.
A number of other CYP enzymes are implicated as minor pathways of dextromethorphan metabolism. CYP2D6 is more effective than CYP3A4 at N-demethylation of dextromethorphan, but since the average individual has a much lower CYP2D6 content in the liver compared to CYP3A4, most N-demethylation of dextromethorphan is catalyzed by CYP3A4.
Chemistry
Dextromethorphan is the dextrorotatory enantiomer of levomethorphan, which is the methyl ether of levorphanol, both opioid analgesics. It is named according to IUPAC rules as (+)-3-methoxy-17-methyl-9α,13α,14α-morphinan. As its pure form, dextromethorphan occurs as an odorless, opalescent white powder. It is freely soluble in chloroform and insoluble in water; the hydrobromide salt is water-soluble up to 1.5 g/100 mL at 25 °C. Dextromethorphan is commonly available as the monohydrated hydrobromide salt, however some newer extended-release formulations contain dextromethorphan bound to an ion-exchange resin based on polystyrene sulfonic acid. Dextromethorphan's specific rotation in water is +27.6° (20 °C, Sodium D-line).
Synthesis
Several routes exist for the synthesis of Dextromethorphan. Even though many of the syntheses have been known since the middle of the 20th century, researchers are still working today to further develop the synthesis of Dextromethorphan and, for example, to make it more environmentally friendly.
This includes the synthesis by means of ionic liquids.
Racemate separation
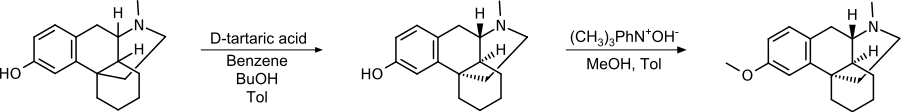
Since only one of the stereoisomers has the desired effect, the separation of a racemic mixture of hydroxy N- methyl morphinan using tartaric acid and subsequent methylation of the hydroxyl group is a suitable method. By using (D)-tartrate, the (+)-isomer remains as the product.
This synthetic pathway was patented by Roche in 1950.
Traditional synthesis
The traditional synthetic route uses Raney nickel and has been further improved over time, for example by the use of ibuprofen and AlCl3.
Overall, it is a cost-effective method with moderate reaction conditions that is easy to handle and suitable for industrial production.
Grewe's cyclization
Grewe's cyclization is easier to handle in terms of the chemicals used, produces higher yields and higher purity of the product.
Improved Grewe's cyclization
Formylation prior to cyclization avoids ether cleavage as a side reaction and yields higher than without N-substitution or N-methylation. In this example, the purification was done by formation of a brucine salt.
This process has also been patented by Roche.
History
The racemic parent compound racemorphan was first described in a Swiss and US patent application from Hoffmann-La Roche in 1946 and 1947, respectively; a patent was granted in 1950. A resolution of the two isomers of racemorphan with tartaric acid was published in 1952, and dextromethorphan was successfully tested in 1954 as part of US Navy and CIA-funded research on nonaddictive substitutes for codeine. Dextromethorphan was approved by the FDA in 1958 as an over-the-counter antitussive. As had been initially hoped, dextromethorphan was a solution for some of the problems associated with the use of codeine phosphate as a cough suppressant, such as sedation and opiate dependence, but like the dissociative anesthetics phencyclidine and ketamine, dextromethorphan later became associated with nonmedical use.
During the 1960s and 1970s, dextromethorphan became available in an over-the-counter tablet form by the brand name Romilar. In 1973, Romilar was taken off the shelves after a burst in sales because of frequent misuse. A few years later, products with an unpleasant taste were introduced (such as Robitussin, Vicks-44, and Dextrotussion), but later the same manufacturers began producing products with a better taste. The advent of widespread internet access in the 1990s allowed users to rapidly disseminate information about dextromethorphan, and online discussion groups formed around use and acquisition of the drug. As early as 1996, dextromethorphan hydrobromide powder could be purchased in bulk from online retailers, allowing users to avoid consuming dextromethorphan in syrup preparations.
FDA panels considered moving dextromethorphan to prescription status due to its potential for abuse, but voted against the recommendation in September 2010, citing lack of evidence that making it prescription-only would curb abuse. Some states have restricted the sale of dextromethorphan to adults or put other restrictions on its purchase in place, similar to those for pseudoephedrine. As of January 1, 2012, dextromethorphan is prohibited for sale to minors in the State of California and in the State of Oregon as of January 1, 2018, except with a doctor's prescription. Several other states have also begun regulating sales of dextromethorphan to minors.
In Indonesia, the National Agency of Drug and Food Control (BPOM-RI) prohibited single-component dextromethorphan drug sales with or without prescription. Indonesia is the only country in the world that makes single-component dextromethorphan illegal even by prescription and violators may be prosecuted by law. National Anti-Narcotics Agency (BNN RI) has even threatened to revoke pharmacies' and drug stores' licenses if they still stock dextromethorphan, and will notify the police for criminal prosecution. As a result of this regulation, 130 medications have been withdrawn from the market, but those containing multicomponent dextromethorphan can still be sold over the counter.
Society and culture
Marketing
It may be used in generic labels and store brands, Benylin DM, Mucinex DM, Camydex-20 tablets, Robitussin, NyQuil, Dimetapp, Vicks, Coricidin, Delsym, TheraFlu, Charcoal D, Cinfatós and others. It has been used in counterfeit medications.
Recreational use
Over-the-counter preparations containing dextromethorphan have been used in manners inconsistent with their labeling, often as a recreational drug. At doses much higher than medically recommended, dextromethorphan and its major metabolite, dextrorphan, acts as an NMDA receptor antagonist, which produces dissociative hallucinogenic states somewhat similar to ketamine and phencyclidine.
It may produce distortions of the visual field – feelings of dissociation, distorted bodily perception, excitement, and a loss of sense of time. Some users report stimulant-like euphoria, particularly in response to music. Dextromethorphan usually provides its recreational effects in a non-linear fashion, so that they are experienced in significantly varied stages. These stages are commonly referred to as "plateaus". These plateaus are numbered from one to four, with the first having the mildest effects to fourth being the most intense. Each plateau is said to come with different related effects and experiences.
The first plateau is said to induce music euphoria and mild stimulation, likened to that of MDMA. The second plateau is likened to a state of being on moderate amounts of alcohol and cannabis at the same time, featuring euphoria, sedation and minor hallucinations. The third plateau induces a significant dissociative state which can often cause anxiety in users. Reaching the fourth plateau is said to cause extreme sedation and a significant hallucinatory state as well as complete dissociation from reality. Teenagers tend to have a higher likelihood to use dextromethorphan-related drugs as they are easier to access, and an easier way to cope with psychiatric disorders.
Research
The combination drug dextromethorphan/quinidine (AVP-923), traditionally used to treat pseudobulbar affect, is under investigation for the treatment of a variety of other neurological and neuropsychiatric conditions including agitation associated with Alzheimer's disease, among others. In 2013, a randomized clinical trial found that dextromethorphan may reduce the overall discomfort and duration of withdrawal symptoms associated with opioid use disorder. When combined with clonidine, dextromethorphan reduced the overall time needed for withdrawal symptoms to peak by 24 hours while reducing severity of symptoms compared to clonidine alone.
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| International | |
|---|---|
| National | |