
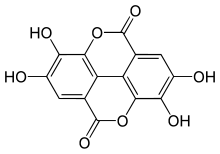
Ellagic acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
|
Preferred IUPAC name
2,3,7,8-Tetrahydroxy[1]benzopyrano[5,4,3-cde][1]benzopyran-5,10-dione | |
| Other names
4,4′,5,5′,6,6′-Hexahydroxydiphenic acid 2,6,2′,6′-dilactone
| |
| Identifiers | |
|
|
|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.827 |
| KEGG |
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H6O8 | |
| Molar mass | 302.197 g/mol |
| Density | 1.67 g/cm3 |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Ellagic acid is a polyphenol found in numerous fruits and vegetables. It is the dilactone of hexahydroxydiphenic acid.
Name
The name comes from the French term acide ellagique, from the word galle spelled backwards because it can be obtained from noix de galle (galls), and to distinguish it from acide gallique (gallic acid). The molecule structure resembles to that of two gallic acid molecules being assembled "head to tail" and bound together by a C–C bond (as in biphenyl, or in diphenic acid) and two lactone links (cyclic carboxylic esters).
Metabolism
Biosynthesis
Plants produce ellagic acid from hydrolysis of tannins such as ellagitannin and geraniin.
Biodegradation
Urolithins are gut flora human metabolites of dietary ellagic acid derivatives. Ellagic acid has low bioavailability, with 90% remaining unabsorbed from the intestines until metabolized by microflora to the more bioavailable urolintins.
History
Ellagic acid was first discovered by chemist Henri Braconnot in 1831.Maximilian Nierenstein prepared this substance from algarobilla, dividivi, oak bark, pomegranate, myrabolams, and valonea in 1905. He also suggested its formation from galloyl-glycine by Penicillium in 1915.Julius Löwe was the first person to synthesize ellagic acid by heating gallic acid with arsenic acid or silver oxide.
Natural occurrences
Ellagic acid is found in oak species such as the North American white oak (Quercus alba) and European red oak (Quercus robur).
The macrophyte Myriophyllum spicatum produces ellagic acid.
Ellagic acid can be found in the medicinal mushroom Phellinus linteus.
In food
The highest levels of ellagic acid are found in raw chestnuts, walnuts, pecans, cranberries, raspberries, strawberries, and grapes, as well as distilled beverages. It is also found in peaches and pomegranates.
| Dietary source | Ellagic acid |
|---|---|
| Fruits (mg/100g fresh weight) | |
| Blackberries | 150 |
| Black raspberries | 90 |
| Boysenberries | 70 |
| Cloudberries | 315.1 |
| Pomegranate | 269.9 |
| Raspberries | 270 |
| Rose hip | 109.6 |
| Strawberries | 77.6 |
| Strawberry jam | 24.5 |
| Yellow raspberries | 1900 |
| Nuts (mg/100g fresh weight) | |
| Pecans | 33 |
| Walnuts | 59 |
| Beverages (mg/L) | |
| Pomegranate juice | 811.1 |
| Cognac | 31–55 |
| Oak-aged red wine | 33 |
| Whiskey | 1.2 |
| Seeds (mg/g) | |
| Black raspberries | 6.7 |
| Red raspberries | 8.7 |
| Boysenberries | 30 |
| Mango | 1.2 |
Research and health claims
Ellagic acid has been marketed as a dietary supplement with various claimed benefits against cancer, heart disease, and other diseases. In the 21st century, numerous U.S.-based supplement companies received FDA warning letters for promoting ellagic acid with false anti-disease claims that violate the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. Ellagic acid has been identified by the FDA as a "fake cancer 'cure'". There is no scientific evidence to support the claims that ellagic acid can treat or prevent cancer.
See also
| CAR |
|
|---|---|
| PXR |
|
| |
