Etynodiol diacetate
 |
|
| Trade names |
Continuin, Demulen, Femulen, Luteonorm, Luto-Metrodiol, Metrodiol, Ovulen, others |
| Other names |
Ethynodiol diacetate; Norethindrol diacetate; 3β-Hydroxynorethisterone 3β,17β-diacetate; 17α-Ethynylestr-4-ene-3β,17β-diyl diacetate; CB-8080; SC-11800 |
Routes of
administration |
By mouth |
| Drug class |
Progestogen; Progestin; Progestogen ester
|
| ATC code |
|
|
| Legal status |
- In general: ℞ (Prescription only)
|
|
[(3S,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-17-acetyloxy-17-ethynyl-13-methyl-2,3,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,14,15,16-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-yl] acetate
|
| CAS Number |
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| PubChem SID
|
|
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.005.496
|
|
| Formula |
C24H32O4
|
| Molar mass |
384.516 g·mol−1
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
O=C(O[C@@H]4/C=C3\[C@@H]([C@H]2CC[C@]1([C@@H](CC[C@]1(C#C)OC(=O)C)[C@@H]2CC3)C)CC4)C
|
InChI=1S/C24H32O4/c1-5-24(28-16(3)26)13-11-22-21-8-6-17-14-18(27-15(2)25)7-9-19(17)20(21)10-12-23(22,24)4/h1,14,18-22H,6-13H2,2-4H3/t18-,19-,20+,21+,22-,23-,24-/m0/s1 Key:ONKUMRGIYFNPJW-KIEAKMPYSA-N
|
Etynodiol diacetate, or ethynodiol diacetate, sold under the brand names Demulen and Femulen among others, is a progestin medication which is used in birth control pills. The medication is available only in combination with an estrogen. It is taken by mouth.
Etynodiol diacetate is a progestin, or a synthetic progestogen, and hence is an agonist of the progesterone receptor, the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. It has weak androgenic and estrogenic activity and no other important hormonal activity. The medication is a prodrug of norethisterone in the body, with etynodiol occurring as an intermediate.
Etynodiol, a related compound, was discovered in 1954, and etynodiol diacetate was introduced for medical use in 1965. The medication remains available today only in the United States, Canada, and a few other countries.
Medical uses
Etynodiol diacetate is used in combination with an estrogen such as ethinylestradiol or mestranol in combined oral contraceptives for women.
Side effects
Pharmacology
Etynodiol diacetate is virtually inactive in terms of affinity for the progesterone and androgen receptors and acts as a rapidly converted prodrug of norethisterone, with etynodiol occurring as an intermediate. Upon oral administration and during first-pass metabolism in the liver, etynodiol diacetate is rapidly converted by esterases into etynodiol, which is followed by oxygenation of the C3 hydroxyl group to produce norethisterone. In addition to its progestogenic activity, etynodiol diacetate has weak androgenic activity, and, unlike most progestins but similarly to norethisterone and noretynodrel, also has some estrogenic activity.
The pharmacokinetics of etynodiol diacetate have been reviewed.
Relative affinities (%) of norethisterone, metabolites, and prodrugs
| Compound |
Typea
|
PR |
AR |
ER |
GR |
MR |
SHBG |
CBG
|
| Norethisterone |
– |
67–75 |
15 |
0 |
0–1 |
0–3 |
16 |
0
|
| 5α-Dihydronorethisterone |
Metabolite |
25 |
27 |
0 |
0 |
? |
? |
?
|
| 3α,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone |
Metabolite |
1 |
0 |
0–1 |
0 |
? |
? |
?
|
| 3α,5β-Tetrahydronorethisterone |
Metabolite |
? |
0 |
0 |
? |
? |
? |
?
|
| 3β,5α-Tetrahydronorethisterone |
Metabolite |
1 |
0 |
0–8 |
0 |
? |
? |
?
|
| Ethinylestradiol |
Metabolite |
15–25 |
1–3 |
112 |
1–3 |
0 |
0.18 |
0
|
| Norethisterone acetate |
Prodrug |
20 |
5 |
1 |
0 |
0 |
? |
?
|
| Norethisterone enanthate |
Prodrug |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
? |
?
|
| Noretynodrel |
Prodrug |
6 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0
|
| Etynodiol |
Prodrug |
1 |
0 |
11–18 |
0 |
? |
? |
?
|
| Etynodiol diacetate |
Prodrug |
1 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
? |
?
|
| Lynestrenol |
Prodrug |
1 |
1 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
? |
?
|
|
Notes: Values are percentages (%). Reference ligands (100%) were promegestone for the PR, metribolone for the AR, estradiol for the ER, dexamethasone for the GR, aldosterone for the MR, dihydrotestosterone for SHBG, and cortisol for CBG. Footnotes: a = Active or inactive metabolite, prodrug, or neither of norethisterone. Sources: See template.
|
Chemistry
Etynodiol diacetate, also known as 3β-hydroxy-17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone 3β,17β-diaceate, 3β-hydroxynorethisterone 3β,17β-diacetate, or 17α-ethynylestr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3β,17β-diacetate, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of testosterone. It is specifically a derivative of 19-nortestosterone and 17α-ethynyltestosterone, or of norethisterone (17α-ethynyl-19-nortestosterone), in which the C3 ketone group has been dehydrogenated into a C3β hydroxyl group and acetate esters have been attached at the C3β and C17β positions. Etynodiol diacetate is the 3β,17β-diacetate ester of etynodiol (17α-ethynylestr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol).
Synthesis
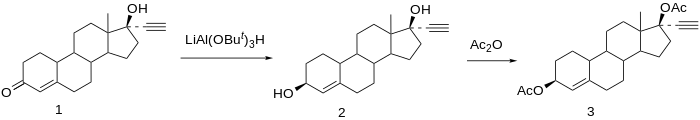
Chemical syntheses of etynodiol diacetate have been published.
Reduction of norethisterone (1) affords the 3,17-diol. The 3β-hydroxy compound is the desired product; since reactions at C3 do not show nearly the stereoselectivity as those at C17 by virtue of the relative lack of stereo-directing proximate substituents, the formation of the desired isomer is engendered by use of a bulky reducing agent, lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride. Acetylation of the 3β,17β-diol affords etynodiol diacetate (3).
History
Etynodiol was first synthesized in 1954, via reduction of norethisterone, and etynodiol diacetate was introduced for medical use in 1965.
Society and culture
Generic names
Etynodiol diacetate is the generic name of the drug (the INN of its free alcohol form is etynodiol), while ethynodiol diacetate is its USAN, BAN, and JAN. It is also known by its former developmental code names CB-8080 and SC-11800.
Brand names
Etynodiol diacetate is or has been marketed under brand names including Conova, Continuin, Demulen, Femulen, Kelnor, Luteonorm, Luto-Metrodiol, Metrodiol, Ovulen, Soluna, Zovia, and others.
Availability
Etynodiol diacetate remains marketed in only a few countries, including the United States, Canada, Argentina, and Oman.
|
|---|
|
|
|---|
Androgens
(incl. AAS) |
|
| Antiandrogens |
|
AR antagonists
|
|
Steroidogenesis
inhibitors |
|
| Antigonadotropins |
-
D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
-
Estrogens (e.g., bifluranol, diethylstilbestrol, estradiol, estradiol esters, ethinylestradiol, ethinylestradiol sulfonate, paroxypropione)
-
GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin)
-
GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix)
-
Progestogens (incl., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, gestonorone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate)
|
| Others |
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Estrogens |
|
ER agonists |
-
Steroidal: Alfatradiol
- Certain androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone, nandrolone esters) (via estrogenic metabolites)
- Certain progestins (e.g., norethisterone, noretynodrel, etynodiol diacetate, tibolone)
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol acetate
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Epiestriol
- Epimestrol
- Esterified estrogens
-
Estetrol†
- Estradiol
-
Estradiol esters (e.g., estradiol acetate, estradiol benzoate, estradiol cypionate, estradiol enanthate, estradiol undecylate, estradiol valerate, polyestradiol phosphate, estradiol ester mixtures (Climacteron))
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estriol
-
Estriol esters (e.g., estriol succinate, polyestriol phosphate)
- Estrogenic substances
- Estrone
-
Estrone esters
-
Ethinylestradiol#
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Nilestriol
-
Prasterone (dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
- Promestriene
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
|
| Progonadotropins |
|
|
| Antiestrogens |
ER antagonists
(incl. SERMs/SERDs) |
|
| Aromatase inhibitors |
|
| Antigonadotropins |
-
Androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, nandrolone esters, oxandrolone, fluoxymesterone)
-
D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
-
GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin, goserelin)
-
GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix, elagolix)
-
Progestogens (e.g., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate)
|
| Others |
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
|
|
|---|
| ER |
| Agonists |
-
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Fluoroestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 11β-Chloromethylestradiol
- 11β-Methoxyestradiol
- 15α-Hydroxyestradiol
- 16-Ketoestradiol
- 16-Ketoestrone
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β-Hydroxyestrone
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
-
17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol
- 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
-
Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
-
Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- ent-Estradiol
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
-
Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
-
Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estrogenic substances
- Estromustine
-
Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
-
Ethinylandrostenediol
-
Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
-
Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
-
Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
-
Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
-
Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, epicatechin, equol, formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, liquiritigenin, mirificin, myricetin, naringenin, penduletin, pinocembrin, prunetin, puerarin, quercetin, tectoridin, tectorigenin)
- Lavender oil
-
Lignans (e.g., enterodiol, enterolactone, nyasol (cis-hinokiresinol))
-
Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium)
-
Pesticides (e.g., alternariol, dieldrin, endosulfan, fenarimol, HPTE, methiocarb, methoxychlor, triclocarban, triclosan)
-
Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis), diosgenin, guggulsterone)
-
Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol)
-
Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol))
-
Steroid-like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol, miroestrol)
-
Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol, rhaponticin)
-
Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., BPA, BPF, BPS), DDT, parabens, PBBs, PHBA, phthalates, PCBs)
- Others (e.g., agnuside, rotundifuran)
|
Mixed
(SERMs) |
|
| Antagonists |
-
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|
| GPER |
| Agonists |
|
| Antagonists |
|
| Unknown |
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| PR |
| Agonists |
-
Testosterone derivatives: Progestins: 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone
- 6,6-Difluoronorethisterone acetate
- 17α-Allyl-19-nortestosterone
- Allylestrenol
- Altrenogest
- Chloroethynylnorgestrel
- Cingestol
- Danazol
- Desogestrel
- Dienogest
-
Ethinylandrostenediol
- Ethisterone
- Ethynerone
- Etonogestrel
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Gestodene
- Gestrinone
- Levonorgestrel
-
Levonorgestrel esters (e.g., levonorgestrel butanoate)
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Metynodiol
- Metynodiol diacetate
- Norelgestromin
- Norethisterone (norethindrone)
-
Norethisterone esters (e.g., norethisterone acetate, norethisterone enanthate)
- Noretynodrel
- Norgesterone
- Norgestimate
- Norgestrel
- Norgestrienone
- Norvinisterone
- Oxendolone
- Quingestanol
- Quingestanol acetate
- Tibolone
- Tigestol
-
Tosagestin; Anabolic–androgenic steroids: 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone
- 11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone dodecylcarbonate
- 19-Nor-5-androstenediol
- 19-Nor-5-androstenedione
- 19-Nordehydroepiandrosterone
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Bolandione
- Dimethisterone
- Dienedione
- Dienolone
- Dimethandrolone
- Dimethandrolone buciclate
- Dimethandrolone dodecylcarbonate
- Dimethandrolone undecanoate
- Dimethyldienolone
- Dimethyltrienolone
- Ethyldienolone
- Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol)
- Methyldienolone
- Metribolone (R-1881)
- Methoxydienone (methoxygonadiene)
- Mibolerone
- Nandrolone
-
Nandrolone esters (e.g., nandrolone decanoate, nandrolone phenylpropionate)
- Norethandrolone
- Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethandrolone, normethisterone)
- RU-2309
- Tetrahydrogestrinone
- Trenbolone (trienolone)
-
Trenbolone esters (e.g., trenbolone acetate, trenbolone enanthate)
- Trendione
- Trestolone
- Trestolone acetate
|
Mixed
(SPRMs) |
|
| Antagonists |
|
|
mPR
(PAQR) |
|
|
|