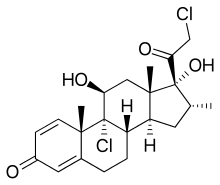
Mometasone
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nasonex, Asmanex, Elocon, others |
| Other names | LAS-41002, 9α,21-Dichloro-11β,17α-dihydroxy-16α-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17α-(2-furoate) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Topical, inhalation (nasal spray) |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; Glucocorticoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Nasal spray is virtually undetectable in plasma; but systemic availability is comparable to fluticasone |
| Protein binding | 98% to 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 5.8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.125.600 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H28Cl2O4 for mometasone C27H30O6Cl2 as furoate |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
|
| |
Mometasone, also known as mometasone y 3 s, is a steroid medication used to treat certain skin conditions, hay fever, and asthma. Specifically it is used to prevent rather than treat asthma attacks. It can be applied to the skin, inhaled, or used in the nose. Mometasone furoate, not mometasone, is used in medical products.
Common side effects when used for asthma includes asthma and thrush. It is therefore recommended to rinse the mouth after use. Long term use may increase the risk for glaucoma and cataracts. Common side effects when used in the nose includes upper respiratory tract infections and nose bleeds. Common side effects when applied on the skin include acne, skin atrophy, and itchiness. It works by decreasing inflammation.
Mometasone furoate was patented in 1981 and came into medical use in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 231st most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 1 million prescriptions.
Medical uses
Mometasone furoate is used in the treatment of inflammatory skin disorders (such as eczema and psoriasis) (topical form), allergic rhinitis (such as hay fever) (topical form), asthma (inhalation form) for patients unresponsive to less potent corticosteroids, and penile phimosis. In terms of steroid strength, it is more potent than hydrocortisone, and less potent than dexamethasone.
Some low-quality evidence suggests the use of mometasone for symptomatic improvement in children with adenoid hypertrophy.
Mometasone is used to alleviate inflammation and itchiness in skin conditions that respond to treatment with glucocorticoids such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Nasal mometasone is used in adults (including the elderly) and children over two years of age, to diminish the symptoms of hay fever (seasonal allergic rhinitis) and other allergies (perennial rhinitis), including nasal congestion, discharge, pruritus, and sneezing and to treat nasal polyps.
It is not useful for the common cold.
Asthma
Mometasone furoate can be used with formoterol for the treatment of asthma, due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Contraindications
People should not use inhaled mometasone or mometasone nasal spray if:
- glaucoma or cataracts
- hypersensitivity or allergic to any ingredient in mometasone
Those who are using mometasone nasal or inhaled for a long period of time (e.g. more than three months) should get regular eye exams to check for glaucoma and cataracts and should take precautions to avoid infections such as taking a vitamin D supplement, staying away from those with an infection (chickenpox, measles, colds or flu, COVID-19), washing foods, hand washing and calling a family doctor at the first sign of a severe infection.
People should not use mometasone topical (skin cream) if:
- hypersensitive or allergic to any ingredient in the skin cream
Mometasone furoate is in class C in terms of safety while use during pregnancy. Therefore, its risks to the baby cannot be ruled out. Therefore, the use in pregnancy is not recommended.
Side effects
The nasal spray form of mometasone may cause the following side effects:
- headache
- Viral upper respiratory infections
- sore throat
- nose bleeds
- cough
- muscle and joint pain
Serious side effects include: Thrush (fungal infection in the nose or throat), slow wound healing, eye problems such as glaucoma or cataracts, weakened immune system (immunodeficiency) which causes an increased susceptibility to infections and adrenal insufficiency.
The inhaled form of mometasone for asthma may cause the following side effects
- headache
- stuffy or runny nose
- dry throat
- swelling of nose, throat and sinuses
- flu like symptoms
- painful menstrual periods
Serious side effects may include: allergic reactions (anaphylaxis), increased risk of osteoporosis, glaucoma and cataracts, thrush in the mouth or throat, growth retardation in children, bronchospasms, adrenal insufficiency and weakened immune system which causes an increased susceptibility to infections.
The topical (skin cream) version may cause:
- burning and itching at the application site
- acne
- changes in skin color
- dryness at application site
- skin sores
The only serious side effect that is known with mometasone topical is adrenal insufficiency.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Mometasone furoate reduces inflammation by causing several effects:
- Reversing the activation of inflammatory proteins
- Activating the secretion of anti-inflammatory proteins
- Stabilizing cell membranes
- Decreasing the influx of inflammatory cells
In addition to the glucocorticoid properties of mometasone furoate, it is a very potent agonist of the progesterone receptor as well as a partial agonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor.
Mechanism of action
Mometasone, like other corticosteroids, possesses anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, and vasoconstrictive properties. For allergies, corticosteroids reduce the allergic reactions in various types of cells (mastocytes and eosinophils) that are responsible for allergic reactions. Mometasone and other corticosteroids circulate in the blood easily, crossing cellular membranes and binding with cytoplasmic receptors, resulting in the transcription and synthesis of proteins. It also inhibits the actions of the enzyme cytochrome P450 2C8 which participates in the activity of monooxygenase.
The inflammation is reduced in decreasing the liberation of hydrolase acids of leukocytes, the prevention of the accumulation macrophages in the sites of inflammation, the interference with adhesion of leukocytes to capillary walls, the reduction of the permeability of the capillary membranes and consequently edema, the reduction of complementary components, inhibition of histamine and kinin liberation, and interference with scar tissue formation. The proliferation of fibroblasts and collagen deposits is also reduced. It is believed that the action of corticosteroid anti-inflammatory agents is bound to inhibitive proteins of phospholipase A2, collectively called lipocortins. The lipocortins, in turn, control the biosynthesis of potent mediators of inflammation as the prostaglandins and leukotrienes, inhibiting the liberation of the molecular precursors of arachidonic acid. Intranasal mometasone alleviates symptoms such as rhinorrhea aquosa, nasal congestion, nasal drip, sneezing, and pharyngeal itching. Topical administration applied to skin reduces the inflammation associated with chronic or acute dermatosis.
Although mometasone furoate does not have significant systemic immunomodulatory effects, it can be considered a local immunosuppressive drug because clinical studies have shown reductions (vs. baseline ) in neutrophils (a white blood cell) in the nasal mucosa. It could be also considered an antihistamine along with its glucocorticoid effects because it significantly reduces histamine and eosinophil cationic protein levels.
Pharmacokinetics
Metabolism
Extensive metabolic hepatic metabolism of mometasone furoate to multiple metabolites occurs. No principal metabolites are detectable in plasma. After in vitro incubation, one of the minor metabolites formed is furoate 6β-hydroxymometasone. In human hepatic microsomes, the formation of these metabolites is regulated by CYP3A4.
Mometasone
Mometasone by itself is a synthetic, steroidal glucocorticoid or corticosteroid that was never marketed. The C17α furoate ester of mometasone, is the marketed medication. Mometasone furoate acts as a prodrug of mometasone. In addition to its glucocorticoid activity, mometasone also has very potent progestogenic activity and acts as a partial agonist of the mineralocorticoid receptor.
Society and culture
Brand names
As of 2016 mometasone furoate was available worldwide in formulations for nasal, oral inhalation, and topical administration, for human and for veterinary use, and in combinations with other drugs, under many brand names. It was available as the single active agent in the following brands: Alcom, Altosone, Asmanex, Atozon, Aureox, Belloseta, Bioelementa, Biometasona, Bloctimo, Borgasone, Breso, Broner, Codermo, Cortynase, Cutimom, Cutizone, Cutticom, Dance, Demoson, Dergentil, Derimod, Dermacortine, Dermaten, Dermome, Dermosona, Dermotasone, Dermovel, Desdek, Ecelecort, Ecural, Edelan, Elica, Elisone, Elisox, Elitasone, Elna, Elocan, Elocom, Elocon, Elocortin, Elofute, Elomet, Elomox, Eloskin, Eloson, Elosone, Elovent, Elox, Etacid, Eversone, Eztom, F-Din, Fenisona, Flazcort, Flogocort, Fremomet, Frondava, Fu Mei Song, Fulmeta, Furo, Furoato de Mometasona, Furoderm, Gistan-H, Honmet, Iflacort, Intercon, Ivoxel, Kalmente, Konex, Ladexol, Lisoder, Logren, Loksin, Lomeane, M-Furo, Makiren, Mefurosan, Melocort, Mena, Mesone, Metacortil, Metactiv, Metaflam, Metagra, Metasafe, Metason, Metasone, Metaspray, Metatop, Metaz, Metmin, Metsone, Midermin, Mifusin, Minyear, Mofacort, Mofulex, Mofur, Mofuroate, Molison, Momate, Momax, Momecon, Momecort, Momecutan, Momederm, MomeGalen, Momegen, Momekort, Momelab, Momentum, Momeplus, Momerid, Momeson, Momesone, Momester, Momet, Mometa, Mometagen, Mometason, Mometasona, Mometasona Furoato, Mometasone Furoate, Mometasone Furoate Hydrate, Mometasonfuroaat, Mometasonfuroat, Mometasoni Furoas, Mometasonum, Mometasyn, Mometasyn, Mometax, Mometazon, Mometazona, Mometazona Fuorat, Mometazonfuroat, Mometix-AQ, Momevate, Momexa, Mommex, Mommox, Momtas, Monaliz, Monez, Monovel, Monovo, Mosone, Motaderm, Motaneal, Movesan, Mtaz, Mundoson, Murozo, Myrey, Narinex, Nasamet, Nasehaler, Nasocure, Nasomet, Nasometin, Nasonex, Nassomet, Nazofix, Nazoster, Netonox, Nexomist, Novasone, Ovison, Ovixan, Oximax, Pharmecort, Pluster, Pronasal, Propel, Prospiril, Pydercon, Rinelon, Rinitek, Rino-Val, Rinobudex, Rinonex, Rinosal, Rinosona, Rinoval, Risonel, Rinocort, Sensicort, Septopic, Silkaren, Soneta, Suavicort, Suqi, Synaller, Tabunex, Topcort, Topison, Uniclar, Uniderm, Vizomet, Yperod, Zalconex, and Zynovate.
Combinations
The following combination drugs are available as of 2022:
- Mometasone and azelastine as Nasaflex
- Mometasone and clotrimazole and gentamicin for veterinary use as Mometamax and Mometavet
- Mometasone and clotrimazole and mupirocin as Derma Q
- Mometasone and florfenicol and terbinafine for veterinary use as Claro
- Mometasone and formoterol as Dulera, Hexaler Bronquial Duo, and Zenhale
- Mometasone and fusidic acid as Bactirest-M, Dermotil Fusid, and Momate-F
- Mometasone and gentamicin and posaconazole for veterinary use as Mometamax Ultra
- Mometasone and hydroquinone and tretinoin as Acnezac-MH
- Mometasone and miconazole as Elica M, Elica-M, and Sensicort-F
- Mometasone and mupirocin as Sensicort-B
- Mometasone and orbifloxacin and posaconazole for veterinary use as Posatex, Posatex voor honden, and Posatex für Hunde
- Mometasone and salicylic acid as Cortimax-S, Elicasal, Elocom Plus, Elosalic, Mezo-S, Momate-S, Momesalic, Momtas-S, Monsalic, and Sensicort-S
- Mometasone and terbinafine as Cutizone-T, Mezo-T, and MomelomTerbi-Humanity
- Mometasone and tiotropium as Tiomom
| Corporate directors | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Subsidiaries | |||
| Products |
|
||
| Facilities | |||
| Publications | |||
| Glucocorticoids |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antiglucocorticoids |
|
||||
| Synthesis modifiers | |||||
| |||||
|
Decongestants and other nasal preparations (R01)
| |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topical |
|
||||||||||
| Systemic use: Sympathomimetics |
|||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| MR |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PR |
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mPR (PAQR) |
|
||||||