
Rimonabant
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Consumer Drug Information |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Undetermined |
| Protein binding | Nearly 100% |
| Metabolism | Hepatic, CYP3A4 involved |
| Elimination half-life | Variable: 6 to 9 days with normal BMI 16 days if BMI >30 |
| Excretion | Fecal (86%) and renal (3%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.210.978 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
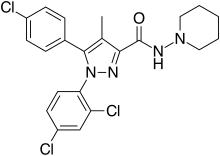
| Formula | C22H21Cl3N4O |
| Molar mass | 463.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug that was first approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was the first drug approved in that class.
History
Rimonabant is a selective CB1receptor blocker and was discovered and developed by Sanofi-Aventis;
On 21 June 2006, the European Commission approved the sale of rimonabant in the then-25-member European Union as a prescription drug for use in conjunction with diet and exercise for patients with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, or patients with a BMI greater than 27 kg/m2 with associated risk factors, such as type 2 diabetes or dyslipidaemia. It was first in its class to be approved anywhere in the world.
Rimonabant was submitted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for approval in the United States in 2005; in 2007, the FDA's Endocrine and Metabolic Drugs Advisory Committee (EMDAC) concluded that Sanofi-Aventis failed to demonstrate the safety of rimonabant and voted against recommending the anti-obesity treatment for approval and two weeks later the company withdrew the application.
The drug was approved in Brazil in April 2007.
In October 2008, the European Medicines Agency recommended the suspension of Acomplia after the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) had determined that the risks of Acomplia outweighed its benefits due to the risk of serious psychiatric problems, including suicide. In November 2008 an advisory committee in Brazil recommended suspension as well, and that month Sanofi-Aventis suspended sale of the drug worldwide. The EMA approval was withdrawn in January 2009. In 2009 India prohibited the manufacture and sale of the drug.
Adverse effects
Data from clinical trials submitted to regulatory authorities showed that rimonabant caused depressive disorders or mood alterations in up to 10% of subjects and suicidal ideation in around 1%, and in Europe it was contraindicated for people with any psychiatric disorder, including depressed or suicidal individuals. Data from a large, randomized, clinical trial (CRESCENDO) with > 9000 patients receiving rimonabant treatment demonstrated a rate of adverse events due to psychiatric disorders (anxiety, depression, depressed mood, or insomnia) of greater than 30%.
Additionally, nausea and upper respiratory tract infections were very common adverse effects (occurring in more than 10% of people); common adverse effects (occurring in between 1% and 10% of people) included gastroenteritis, anxiety, irritability, insomnia and other sleep disorders, hot flushes, diarrhea, vomiting, dry or itchy skin, tendonitis, muscle cramps and spasms, fatigue, flu-like symptoms, and increased risk of falling.
The FDA's advisory committee raised concerns that based on animal data, it appeared that the therapeutic window with regard to CNS toxicity, and specifically seizures was almost nonexistent; the therapeutic dose and the dose that caused seizures in animals appeared to be the same.
When the EMA reviewed postmarketing surveillance data, it found that the risk of psychiatric disorders in people taking rimonabant was doubled.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Rimonabant is an inverse agonist of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Originally thought to be selective for the CB1 receptor, rimonabant was subsequently also found to act as an antagonist of the μ-opioid receptor.
Chemistry
The chemical synthesis of rimonabant is described as follows:
Research
Along with the clinical trials in obesity that generated the data submitted to regulatory authorities, rimonabant was also studied in clinical trials as a potential treatment for other conditions, including diabetes, atherosclerosis, and smoking cessation.
See also
Drinabant, also a cannabinoid developed for prescription drug use that triggered severe psychiatric side effects.
|
Phytocannabinoids (comparison) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endocannabinoids |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists / neocannabinoids |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Allosteric CBR ligands | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Endocannabinoid enhancers (inactivation inhibitors) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Anticannabinoids (antagonists/inverse agonists/antibodies) |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Receptor |
|
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Transporter |
|
||||||||||||
|
Enzyme |
|
||||||||||||
| Others |
|
||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| MOR |
|
|---|---|
| DOR |
|
| KOR |
|
| NOP |
|
| Unsorted | |
| Others |
|
