This is a list of androgens/anabolic steroids (AAS) or testosterone derivatives. Esters are mostly not included in this list; for esters, see here instead. The major classes of testosterone derivatives include the following (as well as combinations thereof):
The last group consists of progestins with mostly only very weak androgenic/anabolic activity.
This article pertains to steroidal androgens; nonsteroidal androgens like the selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) andarine and enobosarm (ostarine) are not included here.
Testosterone derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Cloxotestosterone
|
Testosterone 17-chloral hemiacetal ether
|
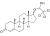
|
✓
|
|
Quinbolone
|
Δ1-Testosterone 17β-cyclopentenyl enol ether
|

|
✓
|
|
Silandrone
|
Testosterone 17β-trimethylsilyl ether
|

|
–
|
Dihydrotestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT); androstanolone, stanolone)
|
4,5α-Dihydrotestosterone
|
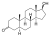
|
✓
|
|
1-Testosterone (dihydro-1-testosterone, dihydroboldenone)
|
4,5α-Dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
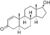
|
–
|
|
11-Ketodihydrotestosterone (11-KDHT)
|
11-Keto-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
–
|
|
Drostanolone
|
2α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Epitiostanol (epithioandrostanol)
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Mesterolone
|
1α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
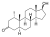
|
✓
|
|
Metenolone (methenolone, methylandrostenolone)
|
1-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Nisterime
|
2α-Chloro-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 3-O-(p-nitrophenyl)oxime
|

|
–
|
|
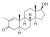
Stenbolone
|
2-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
✓
|
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Mepitiostane
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone 17β-(1-methoxycyclopentane) ether
|

|
✓
|
|
Mesabolone
|
4,5α-Dihydro-δ1-testosterone 17β-(1-methoxycyclohexane) ether
|

|
–
|
|
Prostanozol
|
2'H-5α-Androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol 17β-tetrahydropyran ether
|

|
–
|
Azine dimers
19-Nortestosterone (nandrolone) derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Esters
17α-Alkylated testosterone derivatives
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Ethers
17α-Alkylated dihydrotestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
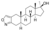
Androisoxazole
|
17α-Methyl-5α-androstano[3,2-c]isoxazol-17β-ol
|
|
✓
|
|
Desoxymethyltestosterone
|
3-Deketo-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ2-testosterone
|

|
–
|
|
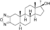
Furazabol
|
17α-Methyl-5α-androstano[2,3-c][1,2,5]oxadiazol-17β-ol
|
|
✓
|
|
Mestanolone (methyl-DHT)
|
17α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Methasterone (methyldrostanolone)
|
2α,17α-Dimethyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|

|
–
|
|
Methyl-1-testosterone (methyldihydro-1-testosterone)
|
17α-Methyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|

|
–
|
|
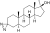
Methyldiazinol
|
3-Azi-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
–
|
|
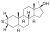
Methylepitiostanol
|
2α,3α-Epithio-3-deketo-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
–
|
|
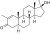
Methylstenbolone
|
2,17α-Dimethyl-4,5α-dihydro-δ1-testosterone
|
|
–
|
|
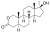
Oxandrolone
|
2-Oxa-17α-methyl-4,5α-dihydrotestosterone
|
|
✓
|
|
Oxymetholone
|
2-Hydroxymethylene-4,5α-dihydro-17α-methyltestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Stanozolol
|
17α-Methyl-2'H-5α-androst-2-eno[3,2-c]pyrazol-17β-ol
|

|
✓
|
Prodrugs
Azine dimers
17α-Alkylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Dimethyltrienolone (7α,17α-dimethyltrenbolone)
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|

|
–
|
|
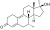
Dimethyldienolone (7α,17α-dimethyldienolone)
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
|
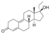
Ethyldienolone
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
|
Ethylestrenol (ethylnandrol)
|
17α-Ethyl-3-deketo-19-nortestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
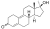
Methyldienolone
|
17α-Methyl-19-nor-δ9-testosterone
|
|
–
|
|
Methylhydroxynandrolone (MOHN, MHN)
|
4-Hydroxy-17α-methyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
–
|
|
Metribolone (methyltrienolone, R-1881)
|
17α-Methyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|

|
–
|
|
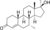
Mibolerone
|
7α,17α-Dimethyl-19-nortestosterone
|
|
✓
|
|
Norboletone
|
17α-Ethyl-18-methyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
–
|
|
Norethandrolone (ethylnandrolone, ethylestrenolone)
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
Normethandrone (methylestrenolone, normethisterone)
|
17α-Methyl-19-nortestosterone
|

|
✓
|
|
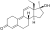
RU-2309 (18-methymetribolone, 17α-methyl-THG)
|
17α,18-Dimethyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|
|
–
|
|
Tetrahydrogestrinone (THG)
|
17α-Ethyl-18-methyl-19-nor-δ9,11-testosterone
|

|
–
|
Prohormone-like
Prodrugs
Esters
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Propetandrol
|
17α-Ethyl-19-nortestosterone 3-propionate
|

|
✓
|
17α-Vinylated testosterone derivatives
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Vinyltestosterone
|
17α-Ethenyltestosterone
|

|
–
|
17α-Vinylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
The 17α-ethenylated (vinylated) testosterone derivative norvinisterone (vinylnortestosterone) is much more potent as an AAS than the 17α-ethynylated testosterone derivatives and is intermediate in potency between the 17α-ethynylated progestins and conventional AAS, with approximately one-third and one-fifth of the respective androgenic and anabolic activity of nandrolone in animal bioassays.
Vinyltestosterone has been described as a weak AAS, though stronger than its 17α-ethynylated analogue ethisterone.
17α-Ethynylated testosterone derivatives
17α-Ethynylated 19-nortestosterone derivatives
Prodrugs
Ethers
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Quingestanol
|
4-Hydro-19-nor-δ3,5-testosterone 3-cyclopentyl ether?
|

|
–
|
Esters
Ethers and esters
| Compound
|
Chemical name
|
Structure
|
Marketed
|
|
Quingestanol acetate
|
4-Hydro-17α-ethynyl-19-nor-δ3,5-testosterone 3-cyclopentyl ether 17β-acetate?
|

|
✓
|
17α-Ethynylated testosterone derivatives are potent progestins with only very weak androgenic/anabolic activity and are used as oral contraceptives or for the treatment of gynecological conditions in women. They are invariably classified as progestins rather than as AAS. However, these progestins are testosterone derivatives and do have significant androgenic/anabolic activity, sometimes producing acne and other mild androgenic effects in women. Conversely, in men, these drugs may actually have functional antiandrogen effects due to their potent progestogenic and hence antigonadotropic activity and capacity to suppress gonadal testosterone production.
See also
? = Chemical names that are unverified.
Further reading
-
Kicman, A T (2008). "Pharmacology of anabolic steroids". British Journal of Pharmacology. 154 (3): 502–521. doi:10.1038/bjp.2008.165. ISSN 0007-1188. PMC 2439524. PMID 18500378.
-
Fragkaki AG, Angelis YS, Koupparis M, Tsantili-Kakoulidou A, Kokotos G, Georgakopoulos C (2009). "Structural characteristics of anabolic androgenic steroids contributing to binding to the androgen receptor and to their anabolic and androgenic activities. Applied modifications in the steroidal structure". Steroids. 74 (2): 172–97. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2008.10.016. PMID 19028512. S2CID 41356223.
-
McRobb L, Handelsman DJ, Kazlauskas R, Wilkinson S, McLeod MD, Heather AK (2008). "Structure-activity relationships of synthetic progestins in a yeast-based in vitro androgen bioassay". J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 110 (1–2): 39–47. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.10.008. PMID 18395441. S2CID 5612000.
|
|
|---|
Androgens
(incl. AAS) |
|
| Antiandrogens |
|
AR antagonists
|
|
Steroidogenesis
inhibitors |
|
| Antigonadotropins |
-
D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
-
Estrogens (e.g., bifluranol, diethylstilbestrol, estradiol, estradiol esters, ethinylestradiol, ethinylestradiol sulfonate, paroxypropione)
-
GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin)
-
GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix)
-
Progestogens (incl., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, gestonorone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate)
|
| Others |
|
|
|


