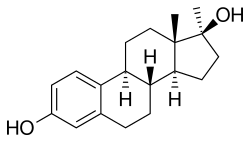
Methylestradiol
 |
 |
|
| Trade names |
Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, Renodiol |
| Other names |
NSC-52245; 17α-Methylestradiol; 17α-ME; 17α-Methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol |
Routes of
administration |
By mouth
|
| Drug class |
Estrogen |
|
(8R,9S,13S,14S,17S)-13,17-dimethyl-7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16-octahydro-6H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-3,17-diol
|
| CAS Number |
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII |
|
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChEMBL |
|
| ECHA InfoCard |
100.005.572
|
|
| Formula |
C19H26O2
|
| Molar mass |
286.415 g·mol−1
|
| 3D model (JSmol) |
|
CC12CCC3C(C1CCC2(C)O)CCC4=C3C=CC(=C4)O
|
InChI=1S/C19H26O2/c1-18-9-7-15-14-6-4-13(20)11-12(14)3-5-16(15)17(18)8-10-19(18,2)21/h4,6,11,15-17,20-21H,3,5,7-10H2,1-2H3/t15-,16-,17+,18+,19+/m1/s1 Key:JXQJDYXWHSVOEF-GFEQUFNTSA-N
|
Methylestradiol, sold under the brand names Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, and Renodiol, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is formulated in combination with normethandrone, a progestin and androgen/anabolic steroid medication. Methylestradiol is taken by mouth.
Side effects of methylestradiol include nausea, breast tension, edema, and breakthrough bleeding among others. It is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptors, the biological target of estrogens like estradiol.
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed in Brazil, Venezuela, and Indonesia. In addition to its use as a medication, methylestradiol has been studied for use as a radiopharmaceutical for the estrogen receptor.
Medical uses
Methylestradiol is used in combination with the progestin and androgen/anabolic steroid normethandrone (methylestrenolone) in the treatment of menopausal symptoms.
Available forms
Methylestradiol is marketed in combination with normethandrone in the form of oral tablets containing 0.3 mg methylestradiol and 5 mg normethandrone.
Side effects
Side effects of methylestradiol include nausea, breast tension, edema, and breakthrough bleeding.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Methylestradiol is an estrogen, or an agonist of the estrogen receptor. It shows somewhat lower affinity for the estrogen receptor than estradiol or ethinylestradiol.
Methylestradiol is an active metabolite of the androgens/anabolic steroids methyltestosterone (17α-methyltestosterone), metandienone (17α-methyl-δ1-testosterone), and normethandrone (17α-methyl-19-nortestosterone), and is responsible for their estrogenic side effects, such as gynecomastia and fluid retention.
Pharmacokinetics
Due to the presence of its C17α methyl group, methylestradiol cannot be deactivated by oxidation of the C17β hydroxyl group, resulting in improved metabolic stability and potency relative to estradiol. This is analogous to the case of ethinylestradiol and its C17α ethynyl group.
Chemistry
Methylestradiol, or 17α-methylestradiol (17α-ME), also known as 17α-methylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is a synthetic estrane steroid and a derivative of estradiol. It is specifically the derivative of estradiol with a methyl group at the C17α positions. Closely related steroids include ethinylestradiol (17α-ethynylestradiol) and ethylestradiol (17α-ethylestradiol). The C3 cyclopentyl ether of methylestradiol has been studied and shows greater oral potency than methylestradiol in animals, similarly to quinestrol (ethinylestradiol 3-cyclopentyl ether) and quinestradol (estriol 3-cyclopentyl ether).
History
Methylestradiol was first marketed, alone as Follikosid and in combination with methyltestosterone as Klimanosid, in 1955.
Society and culture
Generic names
Methylestradiol has not been assigned an INN or other formal name designations. Its generic name in English and German is methylestradiol, in French is méthylestradiol, and in Spanish is metilestadiol. It is also known as 17α-methylestradiol.
Brand names
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed under the brand names Ginecosid, Ginecoside, Mediol, and Renodiol, all in combination with normethandrone.
Availability
Methylestradiol is or has been marketed in Brazil, Venezuela, and Indonesia.
|
|
|---|
| Estrogens |
|
ER agonists |
-
Steroidal: Alfatradiol
- Certain androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone, nandrolone esters) (via estrogenic metabolites)
- Certain progestins (e.g., norethisterone, noretynodrel, etynodiol diacetate, tibolone)
- Clomestrone
- Cloxestradiol acetate
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Epiestriol
- Epimestrol
- Esterified estrogens
-
Estetrol†
- Estradiol
-
Estradiol esters (e.g., estradiol acetate, estradiol benzoate, estradiol cypionate, estradiol enanthate, estradiol undecylate, estradiol valerate, polyestradiol phosphate, estradiol ester mixtures (Climacteron))
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estriol
-
Estriol esters (e.g., estriol succinate, polyestriol phosphate)
- Estrogenic substances
- Estrone
-
Estrone esters
-
Ethinylestradiol#
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Nilestriol
-
Prasterone (dehydroepiandrosterone; DHEA)
- Promestriene
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
|
| Progonadotropins |
|
|
| Antiestrogens |
ER antagonists
(incl. SERMs/SERDs) |
|
| Aromatase inhibitors |
|
| Antigonadotropins |
-
Androgens/anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone, testosterone esters, nandrolone esters, oxandrolone, fluoxymesterone)
-
D2 receptor antagonists (prolactin releasers) (e.g., domperidone, metoclopramide, risperidone, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, sulpiride)
-
GnRH agonists (e.g., leuprorelin, goserelin)
-
GnRH antagonists (e.g., cetrorelix, elagolix)
-
Progestogens (e.g., chlormadinone acetate, cyproterone acetate, gestonorone caproate, hydroxyprogesterone caproate, medroxyprogesterone acetate, megestrol acetate)
|
| Others |
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| ER |
| Agonists |
-
Steroidal: 2-Hydroxyestradiol
- 2-Hydroxyestrone
- 3-Methyl-19-methyleneandrosta-3,5-dien-17β-ol
- 3α-Androstanediol
- 3α,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3β,5α-Dihydrolevonorgestrel
- 3α-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Hydroxytibolone
- 3β-Androstanediol
- 4-Androstenediol
- 4-Androstenedione
- 4-Fluoroestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestradiol
- 4-Hydroxyestrone
- 4-Methoxyestradiol
- 4-Methoxyestrone
- 5-Androstenediol
- 7-Oxo-DHEA
- 7α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 7α-Methylestradiol
- 7β-Hydroxyepiandrosterone
- 8,9-Dehydroestradiol
- 8,9-Dehydroestrone
- 8β-VE2
- 10β,17β-Dihydroxyestra-1,4-dien-3-one (DHED)
- 11β-Chloromethylestradiol
- 11β-Methoxyestradiol
- 15α-Hydroxyestradiol
- 16-Ketoestradiol
- 16-Ketoestrone
- 16α-Fluoroestradiol
- 16α-Hydroxy-DHEA
- 16α-Hydroxyestrone
- 16α-Iodoestradiol
- 16α-LE2
- 16β-Hydroxyestrone
- 16β,17α-Epiestriol (16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
-
17α-Estradiol (alfatradiol)
- 17α-Dihydroequilenin
- 17α-Dihydroequilin
- 17α-Epiestriol (16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol)
- 17α-Ethynyl-3α-androstanediol
- 17α-Ethynyl-3β-androstanediol
- 17β-Dihydroequilenin
- 17β-Dihydroequilin
- 17β-Methyl-17α-dihydroequilenin
- Abiraterone
- Abiraterone acetate
- Alestramustine
- Almestrone
-
Anabolic steroids (e.g., testosterone and esters, methyltestosterone, metandienone (methandrostenolone), nandrolone and esters, many others; via estrogenic metabolites)
- Atrimustine
- Bolandiol
- Bolandiol dipropionate
- Butolame
- Clomestrone
-
Cloxestradiol
- Conjugated estriol
- Conjugated estrogens
- Cyclodiol
- Cyclotriol
- DHEA
- DHEA-S
- ent-Estradiol
- Epiestriol (16β-epiestriol, 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol)
- Epimestrol
- Equilenin
- Equilin
- ERA-63 (ORG-37663)
- Esterified estrogens
- Estetrol
-
Estradiol
- Estramustine
- Estramustine phosphate
- Estrapronicate
- Estrazinol
-
Estriol
- Estrofurate
- Estrogenic substances
- Estromustine
-
Estrone
- Etamestrol (eptamestrol)
-
Ethinylandrostenediol
-
Ethinylestradiol
- Ethinylestriol
- Ethylestradiol
- Etynodiol
- Etynodiol diacetate
- Hexolame
- Hippulin
- Hydroxyestrone diacetate
- Lynestrenol
- Lynestrenol phenylpropionate
- Mestranol
- Methylestradiol
- Moxestrol
- Mytatrienediol
- Nilestriol
- Norethisterone
- Noretynodrel
- Orestrate
- Pentolame
- Prodiame
- Prolame
- Promestriene
- RU-16117
- Quinestradol
- Quinestrol
- Tibolone
-
Xenoestrogens: Anise-related (e.g., anethole, anol, dianethole, dianol, photoanethole)
-
Chalconoids (e.g., isoliquiritigenin, phloretin, phlorizin (phloridzin), wedelolactone)
-
Coumestans (e.g., coumestrol, psoralidin)
-
Flavonoids (incl. 7,8-DHF, 8-prenylnaringenin, apigenin, baicalein, baicalin, biochanin A, calycosin, catechin, daidzein, daidzin, ECG, EGCG, epicatechin, equol, formononetin, glabrene, glabridin, genistein, genistin, glycitein, kaempferol, liquiritigenin, mirificin, myricetin, naringenin, penduletin, pinocembrin, prunetin, puerarin, quercetin, tectoridin, tectorigenin)
- Lavender oil
-
Lignans (e.g., enterodiol, enterolactone, nyasol (cis-hinokiresinol))
-
Metalloestrogens (e.g., cadmium)
-
Pesticides (e.g., alternariol, dieldrin, endosulfan, fenarimol, HPTE, methiocarb, methoxychlor, triclocarban, triclosan)
-
Phytosteroids (e.g., digitoxin (digitalis), diosgenin, guggulsterone)
-
Phytosterols (e.g., β-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol)
-
Resorcylic acid lactones (e.g., zearalanone, α-zearalenol, β-zearalenol, zearalenone, zeranol (α-zearalanol), taleranol (teranol, β-zearalanol))
-
Steroid-like (e.g., deoxymiroestrol, miroestrol)
-
Stilbenoids (e.g., resveratrol, rhaponticin)
-
Synthetic xenoestrogens (e.g., alkylphenols, bisphenols (e.g., BPA, BPF, BPS), DDT, parabens, PBBs, PHBA, phthalates, PCBs)
- Others (e.g., agnuside, rotundifuran)
|
Mixed
(SERMs) |
|
| Antagonists |
-
Coregulator-binding modulators: ERX-11
|
|
| GPER |
| Agonists |
|
| Antagonists |
|
| Unknown |
|
|
|


